Trying to get a handle on your Amazon Web Services costs can feel like you're staring at a giant, confusing utility bill. But it all comes down to a simple idea: you only pay for what you turn on and use. Unlike a flat monthly subscription, your AWS bill is a detailed breakdown of every single service you've used, just like your home utility bill shows exactly how much electricity and water you consumed.
What Actually Drives Your Amazon Web Services Costs
Think of your AWS bill as a combination of four different utility services, each adding to your total. Once you can separate them out, you'll know exactly where your money is going. For most businesses, the bulk of their AWS spend falls into four main buckets. Breaking down your bill this way is the first real step to getting your cloud costs under control.
These four pillars are the fundamental building blocks for pretty much any application you can run in the cloud.
- Compute: This is the engine of your cloud setup, the raw processing power you rent from AWS. It’s like paying for the electricity to keep the lights on and the computers running.
- Storage: This is the digital warehouse where you keep all your data. Think of it like renting a storage unit, where your bill depends on how much stuff you’re storing.
- Data Transfer: This is the cost of moving your data around. It's similar to paying postage fees to ship a package from your warehouse to a customer.
- Managed Services: These are the specialized "done-for-you" services that handle complex jobs. It's like hiring a professional plumber instead of trying to fix a burst pipe yourself.
The Cost of Compute Power
For many, compute is the single biggest line item on their AWS bill. The main player here is Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), which gives you virtual servers in the cloud. You're charged based on the server's size, its power, and exactly how long you keep it running, often billed down to the second.
Leaving an EC2 instance running when nobody is using it is the digital version of leaving every light on in an empty office building all weekend. You’re burning money on a resource that isn’t creating any value. This is easily one of the most common ways companies waste money, and it’s why keeping an eye on your compute resources is so important.
Paying for Digital Storage Space
Next up is storage, with the star of the show being Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service). S3 is built for storing "objects", everything from website images and videos to massive data backups. The cost is simple: the more gigabytes of data you store, the more you pay.
For instance, a quick look at the S3 pricing page shows you that costs are tiered. The price per gigabyte actually goes down the more data you store.
This screenshot shows that your first 50 TB costs more per gigabyte than the data you store after that point. Getting familiar with these tiers is a simple but effective way to manage your storage bill.
A classic mistake is treating all data as if it's equally important. Not every file needs to be available in a millisecond. By moving older, less-accessed data to cheaper storage tiers, you can slash your storage costs without losing anything important.
Understanding Data Transfer Fees
Data transfer, often called "data egress," is what you pay to move data out of AWS and onto the public internet. The good news is that moving data into AWS is almost always free. It’s like a shipping company that lets you receive packages for free but charges you every time you send one out.
These egress fees can be a nasty surprise if you're not tracking them. An application serving large video files to users around the world will rack up much higher data transfer costs than an app that just crunches numbers internally within AWS. If you want to dig deeper into how cloud costs work in general, our guide on the total cost of cloud ownership offers a broader perspective.
The Value of Managed Services
Finally, you have managed services like Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) or AWS Lambda. These services are all about convenience. With RDS, AWS takes care of all the painful database admin work: patching, backups, scaling, you name it. With Lambda, you can run code without even thinking about servers.
You're essentially paying for AWS's expertise and for them to handle the operational heavy lifting. It's the same reason you'd hire a specialized contractor for a tricky home renovation instead of doing it yourself. The upfront cost might seem higher than a DIY approach, but it saves you an incredible amount of time and helps you avoid costly mistakes, often making it the cheaper option in the long run.
Choosing the Right AWS Pricing Model to Save Money
Once you get a handle on the main parts of your bill, the next move is picking the right payment plan. AWS offers a few different pricing models, and choosing the right one is one of the most powerful levers you can pull to control your costs. In fact, moving beyond the default "pay as you go" model is your first major step toward serious savings.
Think of it like booking a trip. The standard On-Demand pricing is like walking up to a hotel's front desk and booking a room for the night. You get total flexibility and pay the full rate, but there are zero strings attached. This is perfect for spiky, unpredictable workloads or for when you're just starting out and have no idea what you'll need.
But if you know you're going to be sticking around for a while, you can get a much, much better deal.
AWS Pricing Model Comparison
This table breaks down the main AWS pricing models to help you decide which is best for your workloads, balancing cost, flexibility, and commitment.
| Pricing Model | Best For | Commitment | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand | Unpredictable, short-term workloads or development/testing. Maximum flexibility. | None | 0% |
| Reserved Instances (RIs) | Stable, predictable workloads with consistent usage (e.g., production databases). | 1 or 3 years | Up to 72% |
| Savings Plans | Predictable spend across various services and instance types. More flexibility than RIs. | 1 or 3 years | Up to 72% |
| Spot Instances | Fault-tolerant, non-critical workloads that can be interrupted (e.g., batch jobs, data analysis). | None | Up to 90% |
Choosing the right blend of these models is where the real cost optimization magic happens. A single application might use RIs for its core database, On-Demand instances for its web servers, and Spot Instances for nightly data processing jobs.
Committing to Save with Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
For workloads that are predictable and long-term, Reserved Instances (RIs) offer some hefty discounts. This is like prepaying for a hotel room for a whole year to lock in a deeply discounted rate. You can potentially save up to 72% compared to On-Demand prices. The catch is you have to commit to a specific instance type in a specific region for a one or three-year term.
A more flexible cousin to RIs is Savings Plans. Think of this as buying a gift card for a hotel chain. You commit to spending a certain amount of money per hour for one or three years, and in return, you get a discount on whatever you use. The discount applies across different instance types and even some different services, giving you way more freedom than traditional RIs. You can learn more about how Savings Plans provide flexibility in our detailed guide.
This decision tree helps visualize where your money typically goes, which can help you decide which pricing model is best for your biggest cost drivers.
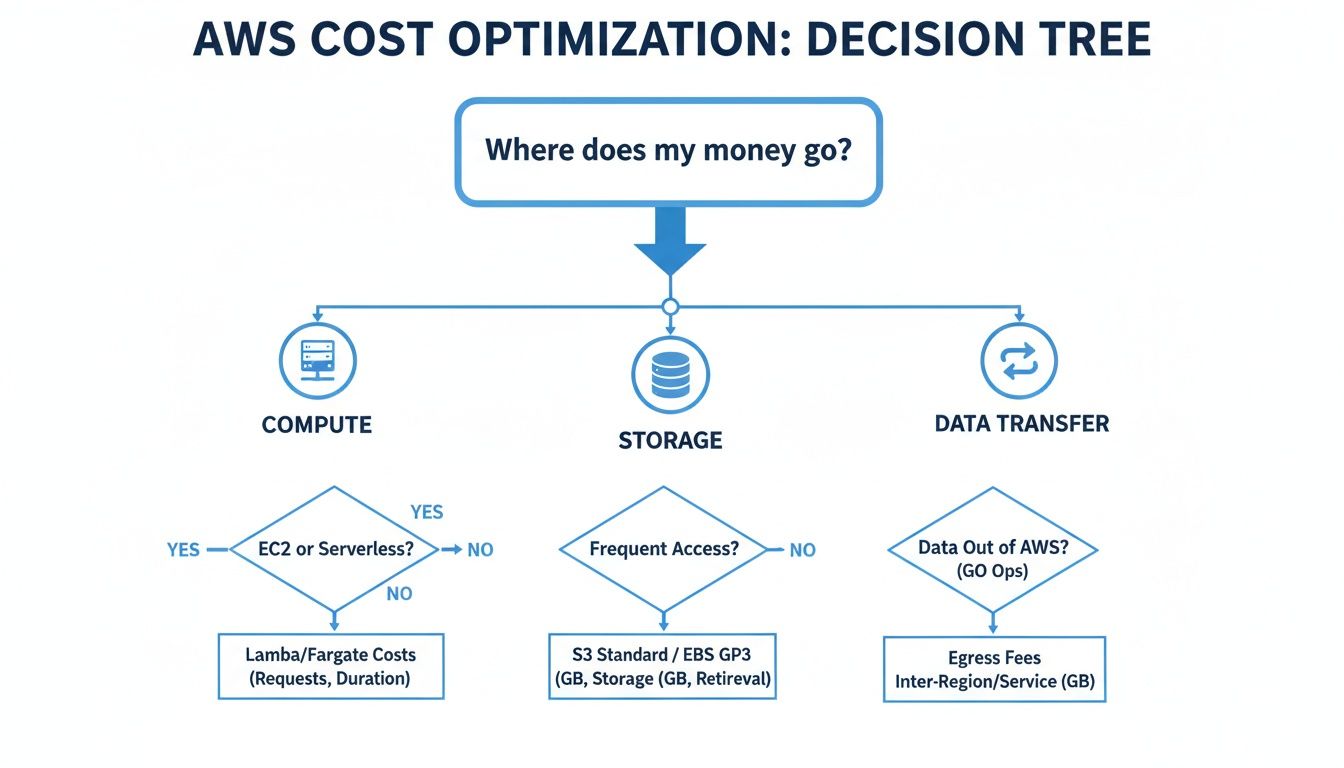
As the graphic shows, compute, storage, and data transfer are usually the big three. This makes your choice of pricing model absolutely critical for getting your costs under control.
Capturing Massive Discounts with Spot Instances
For tasks that can be interrupted without causing a disaster, Spot Instances offer the most dramatic savings around, often slashing costs by up to 90% off On-Demand rates. The analogy here is bidding on an empty, unsold hotel room for the night. You get an unbelievable deal, but you have to be okay with the hotel asking you to leave if a full-price guest suddenly shows up.
Spot Instances let you use AWS's spare, unused compute capacity. They are absolutely perfect for workloads that aren't time-sensitive or mission-critical, like:
- Batch processing jobs
- Large-scale data analysis
- Test and development environments
Because AWS can reclaim these instances with just a two-minute warning, they are a terrible fit for things like production databases or customer-facing applications. But if you use them strategically for the right tasks, you can see a massive drop in your overall AWS bill.
How to Use AWS Cost Explorer for Actionable Insights
Flying blind with cloud spending is a common way organizations get hit with a nasty surprise when the monthly bill lands. Think of AWS Cost Explorer as the GPS for your cloud budget, lighting up the path and showing you exactly where every dollar is going. It takes mountains of raw billing data and turns it into clear, interactive charts that make your amazon web services costs easy to understand.
Instead of getting lost in dense spreadsheets, you can use its visual interface to see spending patterns, filter costs by specific services or project tags, and spot unusual spikes in an instant. This tool is your first line of defense against reactive bill shock. It’s what helps you get ahead of your spending.

The dashboard gives you that crucial high-level view, letting you spot trends, see your most expensive services at a glance, and check how your spending is tracking against forecasts.
Uncovering Cost Anomalies and Trends
The real magic of Cost Explorer is its power to help you play detective with your spending. Let's say you notice your EC2 costs suddenly jumped from last month. Instead of just shrugging your shoulders and accepting the hit, you can drill down into the data with a few clicks.
You can filter the view to isolate that spike and find out exactly what changed. The tool lets you group your costs by:
- Service: Was the spike from EC2, S3, RDS, or something else entirely?
- Region: Did costs shoot up in a specific geographic region?
- Instance Type: Is one particular type of virtual server the culprit?
- Tags: If you’ve tagged resources by project, you can see which team’s spending went up.
This turns a mysterious bill increase into a clear, actionable insight. You might find out a developer accidentally left a powerful, expensive instance running over the weekend or that a new project was launched in a pricier region by mistake.
From Raw Data to Actionable Intelligence
Ultimately, the goal is to stop reacting to bills and start making smart, proactive decisions. By spotting trends that signal waste, you can build a better cost management strategy. For example, a steady climb in your S3 costs might be the nudge you need to finally implement a storage tiering policy to move old data to cheaper storage.
Cost Explorer helps you answer the most important question: "Why did my costs change?" By digging in to find the answer, you build a culture of cost accountability on your team.
And the tool just got a lot better. In November 2023, AWS gave Cost Explorer a major upgrade, extending its historical data access to 14 months by default. This fixed a huge headache for anyone trying to do year-over-year comparisons. Now you can easily graph October 2023 vs. 2022 or analyze a three-year RDS spend without any workarounds.
Setting Up Budgets and Forecasts
Looking at past spending is great, but Cost Explorer also helps you look ahead. You can set up AWS Budgets to get alerts when your costs or usage are on track to blow past your limits. It’s like setting a spending alert on your credit card.
You can create budgets for your total monthly spend, for a specific service like EC2, or even for a project tag. When spending is forecasted to exceed your budget, you’ll get an email or an SNS notification. This gives you time to step in and make changes before the costs spiral. Using these features is a core part of managing AWS costs efficiently.
Proven Strategies to Reduce Your Cloud Spend
Alright, so you've used tools like AWS Cost Explorer and have a handle on your biggest cost drivers. That's a great first step. But seeing where the money goes is only half the battle. Now it's time to actually stop the bleeding.
This is where you move from just looking at reports to making practical changes that deliver real, tangible savings on your amazon web services costs.

We're not talking about complex architectural overhauls. Let's dive into a toolkit of proven tactics that you can implement right away to cut down on that unnecessary spend.
Rightsize Your Instances
Rightsizing is probably the quickest win you can get. It's the simple process of matching your EC2 instances to what they actually need to perform their job. So many teams overprovision resources "just in case," paying for a beast of a server that barely breaks a sweat.
Think of it like paying for a V8 engine in a car you only use for city driving. A simple four-cylinder would get the job done just fine, for a fraction of the cost.
Before and After Rightsizing: A dev team might be running a
t3.xlargeinstance for a test environment, costing them around $120 per month. After checking the CPU and memory usage, they realize at3.mediumis more than enough. That simple switch drops the monthly cost to about $30, a 75% savings on just one resource.
Tools like AWS Compute Optimizer are perfect for this, giving you data-driven recommendations so you can downsize with confidence.
Leverage S3 Storage Tiering
Let's be honest: not all data is created equal. Storing old log files or archived project data on high-performance, expensive storage is like keeping your winter coats in the front-hall closet all summer. It's just a waste of valuable space.
Amazon S3 has different storage classes, each with its own price point and access speed. The best part? You can automate this with S3 Intelligent-Tiering. It keeps an eye on your data's access patterns and automatically moves files that haven't been touched in a while to cheaper, infrequent access tiers.
This little bit of automation makes sure you're only paying top dollar for the data you need right now.
Eliminate Orphaned Resources
In a fast-moving cloud environment, it's incredibly easy to spin up resources for a project and then forget to delete them when you're done. These "orphaned" resources are the silent killers of your cloud budget, quietly racking up charges month after month without providing any value.
Keep an eye out for these common culprits:
- Unattached EBS Volumes: These are virtual hard drives that were once attached to an EC2 instance. When the instance was terminated, the volume stuck around. You're literally paying for storage you can't even access.
- Idle Elastic Load Balancers: A load balancer with no instances registered to it is just sitting there, but it still has an hourly charge.
- Unused Elastic IP Addresses: AWS applies a small fee for Elastic IPs that are in your account but not attached to a running instance. It’s a small charge, but it adds up.
Running a regular audit for these stray resources is like cleaning out your garage. You’ll be shocked at how much junk you can clear out and how much money you'll save immediately.
Optimize Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer fees can be a sneaky, significant chunk of your bill. While getting data into AWS is free, moving it back out to the internet (known as egress) definitely costs money. A few best practices can make a huge difference here.
First, use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Amazon CloudFront. A CDN caches your content in data centers all over the world, closer to your users. When someone requests a file, it's served from the closest "edge location" instead of directly from your S3 bucket. This is almost always cheaper and much faster for the end-user.
Second, try to keep data transfers within the same AWS region whenever you can. Moving data between services in the same Availability Zone is often free, but crossing regional boundaries will cost you. Architecting your apps to minimize that cross-region chatter can lead to some serious savings. To get a deeper dive into managing your total cloud spend, check out this guide to Master Amazon Web Service Cost.
Shut Down Non-Production Resources
This is the big one. One of the single largest sources of waste in the cloud is paying for development, testing, and staging environments to run 24/7. These servers are usually only needed during business hours, which means they sit idle for roughly 128 hours every single week. That's a lot of wasted cash.
By simply shutting down these idle servers on nights and weekends, you can slash their costs by as much as 70%. You can do it manually, sure, but automation is what makes this strategy stick. Implementing a simple "on/off" schedule is often the most effective cost-saving move a company can make, period.
Automating Cost Savings Beyond Native AWS Tools
Manual cost optimization is a great starting point, but it has its limits. Sure, you can manually shut down a few servers or right-size an instance here and there, but that strategy just doesn't scale as your infrastructure grows. Eventually, you hit a wall.
This is where automation becomes your best friend for getting your amazon web services costs under control for good.
One of the quickest wins with automation is scheduling idle resources to shut down. This is especially true for non-production environments like development, testing, and staging. These resources are notorious for racking up costs because they often sit unused for more than half the week, nights and weekends included. Automating their shutdown is a simple way to make sure you only pay for what you’re actually using.
AWS does offer its own tools for this, like the AWS Instance Scheduler. While they’re certainly capable, these native tools come with a steep learning curve and operational headaches that can make them a tough sell for many teams. They are definitely not simple, point-and-click solutions.
The Challenges of Native AWS Schedulers
Let's be clear: native AWS tools are powerful, but they’re built for engineers who are comfortable digging into code, running scripts, and navigating complex permissions. This immediately creates a barrier for non-technical team members who could otherwise be helping you save money.
Here are a few common hurdles you'll face with native solutions:
- A Painful Setup: Deploying something like the Instance Scheduler involves running CloudFormation templates, configuring DynamoDB tables, and setting up Lambda functions. It’s a multi-step, technical process that can be pretty intimidating.
- Scripting Required: Need to customize a schedule or make a one-off exception? Get ready to edit some scripts or JSON configuration files. This isn't exactly user-friendly for a project manager or developer who just wants to turn a server off for the weekend.
- Risky Permissions: To get these tools to work, you often have to grant them sweeping IAM (Identity and Access Management) permissions. If you’re not extremely careful, you could expose your entire AWS account to unnecessary security risks.
Because of all this complexity, the job of managing schedules usually falls on a small group of senior engineers. This creates bottlenecks and severely limits how much your organization can actually save.
How Specialized Platforms Simplify Automation
This is exactly why third-party, specialized platforms have become so popular. They are purpose-built to solve the problems that native tools create by focusing on simplicity, security, and making cost-saving accessible to everyone. Instead of needing a PhD in AWS, you get an intuitive interface that anyone on the team can pick up and use.
These platforms transform cost optimization from a complex engineering task into a simple operational habit. They empower entire teams to participate in saving money, securely and without needing direct access to the core AWS console.
A huge advantage here is role-based access control. You can give a project manager the ability to schedule their team's development servers without giving them permission to touch anything else in your AWS account. This kind of granular control is a game-changer for both security and operational efficiency. Beyond scheduling, you can also explore how to improve operational efficiency with AI to find even more ways to cut cloud waste.
This side-by-side comparison really highlights the key differences between the two approaches.
Specialized Platforms vs Native AWS Scheduling Tools
| Feature | Native AWS Tools (e.g., Instance Scheduler) | Specialized Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Relies on AWS Console, CLI, and scripts. | Simple, intuitive web interface. |
| Setup Process | Requires complex CloudFormation deployment. | Quick setup, often in minutes. |
| Access Control | Requires broad and complex IAM roles. | Granular, role-based access for non-engineers. |
| Ease of Use | Demands technical expertise and scripting. | Easy for anyone to create and manage schedules. |
| Scalability | Can be difficult to manage across many teams. | Designed for multi-team and multi-account use. |
By taking care of all the underlying complexity, specialized tools make automated scheduling a practical reality for any organization, not just those with deep engineering resources. This allows you to lock in predictable, continuous savings, especially from those non-production environments that are notorious for driving up amazon web services costs when left running 24/7.
Frequently Asked Questions About Managing AWS Costs
Getting a handle on your Amazon Web Services costs brings up the same questions time and time again, no matter the size of your team. Nailing down the answers is the first step toward building a culture of cost awareness and making sure your cloud bill actually supports your business goals.
Let's dive into some of the most common questions we hear.
How Can I Accurately Forecast My Future AWS Costs?
Forecasting your AWS spend isn't about gazing into a crystal ball. It’s about making smart, data-backed projections. The best way to do this is by blending your past spending data with your future business plans.
First, you need to become friends with AWS Cost Explorer. It gives you a historical view of your spending, now going back 14 months, which is perfect for spotting trends. Are your costs creeping up by 5% each month? Do you see the same spikes every holiday season? This history is your baseline.
Next, you have to overlay your company's roadmap on top of that data. Think about what’s coming up:
- Launching a new app next quarter? You can bet your compute and database costs are going to climb.
- Got a big marketing push planned? Get ready for a jump in data transfer fees as more people visit your site.
- Archiving a massive dataset? Your S3 costs should drop as you move data from a standard tier to a much cheaper archival one.
When you combine what you know about the past with what you know about the future, your forecast becomes much more reliable. Cost Explorer even has its own forecasting feature that uses machine learning to give you a solid starting point.
What Is the Most Common Mistake Businesses Make with AWS Billing?
Hands down, the single biggest and most expensive mistake is the "set it and forget it" mindset, especially with non-production resources. Your dev, staging, and test environments are almost always the biggest culprits for wasted spend because they’re left running 24/7.
Think about it. Those servers are really only needed during work hours, maybe 40-50 hours a week. But they keep ringing up charges all night, every weekend, and on holidays. That means for every single non-prod instance, you could be paying for 120+ hours of pure idle time each week.
This one oversight can easily bloat your development and testing budget by over 70%. It’s the digital equivalent of leaving the lights on in an empty office building all weekend, a totally avoidable expense that delivers zero value.
This happens so often because relying on people to manually shut things down just doesn't work. Developers forget, priorities change, and those idle resources just keep on running. This is exactly why automating the shutdown of these environments is the most impactful cost-saving move most companies can make.
How Often Should I Review My AWS Cost Optimization Strategy?
Cost optimization isn't a "one and done" project; it’s a continuous loop. How often you review your strategy depends on how big and dynamic your cloud footprint is, but a regular rhythm is key.
A good review cycle has a few different layers:
- Weekly Check-Ins: This is just a quick glance at your AWS Budgets and cost dashboards. The goal here is to catch any wild, unexpected spikes before they turn into a real problem.
- Monthly Deep Dives: Time to roll up your sleeves. Your team should dig into Cost Explorer, see what's driving the most spend, and check if your optimization efforts (like rightsizing or scheduling) are actually working. This is also the perfect time to review your Savings Plans or Reserved Instance coverage.
- Quarterly Strategy Reviews: Now, you zoom out. Are your tagging policies actually being used correctly? Is your governance model effective? This is when you assess if your overall strategy is still aligned with the company’s financial targets and upcoming projects.
The cloud moves fast, and so do your applications. AWS is constantly tweaking its pricing, sometimes dropping costs on high-demand GPU instances by as much as 45%. A strategy that was brilliant six months ago might be leaving money on the table today. A continuous review process ensures you’re always adapting and grabbing every opportunity to save.
Stop wasting money on idle cloud resources. CLOUD TOGGLE makes it simple to automate server schedules, cutting your AWS bill by up to 70% with just a few clicks. Start your free 30-day trial and see how much you can save at https://cloudtoggle.com.




