Resource scheduling is the simple but powerful practice of turning off cloud resources when they are not in use. Think of it like turning off the lights in an empty office to save on the electricity bill. This strategy targets one of the biggest hidden costs in tech: paying for idle infrastructure. It’s a foundational concept in cloud financial management, or FinOps.
What Is Resource Scheduling Explained

At its heart, resource scheduling is a proactive way to clamp down on your cloud bill. Instead of letting services like virtual machines, servers, and databases run 24/7 by default, you define specific "on" and "off" times. This commonsense approach ensures you only pay for compute power when you actually need it.
The best place to start? Non production environments. We're talking about all the infrastructure used for development, testing, staging, and quality assurance (QA). These resources are usually only needed during standard business hours, yet most companies pay for them around the clock.
The Problem of Idle Cloud Resources
Imagine a development team that works Monday to Friday, from 9 AM to 5 PM. Their servers, which are essential for coding and testing, are only truly needed for 40 hours per week. But without a schedule, those servers keep running all night, over the weekend, and during holidays.
That means the infrastructure stays active for all 168 hours in a week, leading to a massive amount of waste. For about 128 hours, the resources just sit there doing nothing while the cloud provider’s billing meter keeps ticking. This is where scheduling becomes a game-changer for any organization trying to get its cloud budget under control.
By implementing a schedule, you stop paying for resources to do nothing. This simple shift in mindset can lead to immediate and substantial savings, often reducing non production cloud costs by up to 75%.
To put this concept into a simple framework, let's break down the core components of resource scheduling.
Resource Scheduling at a Glance
The table below offers a quick summary of what resource scheduling is all about, from the what to the why.
| Component | Description | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Using tools to programmatically start and stop cloud services. | Reduce manual effort and ensure consistency. |
| Schedules | Defining specific "on" and "off" times for resources. | Align infrastructure availability with business needs. |
| Targeting | Identifying non-essential resources, like dev/test environments. | Maximize savings by focusing on the biggest areas of waste. |
| Governance | Setting policies and access controls for scheduling. | Maintain control and prevent accidental downtime. |
Ultimately, these components work together to turn a passive, ongoing expense into a controlled, optimized investment.
Who Benefits From Scheduling
Nearly everyone touching a company's tech stack benefits from a smart scheduling policy. It's not just a niche practice for one department; it delivers value across the entire organization.
Here’s a look at who gets the biggest wins:
- Developers and Engineers: They get to operate within predictable budgets without constantly worrying about accidental overspending from a forgotten test environment.
- IT and DevOps Managers: They gain much better control over cloud infrastructure, can enforce governance rules, and forecast costs with far greater accuracy.
- Financial and FinOps Teams: They see a direct, measurable reduction in the monthly cloud bill, freeing up capital that can be put toward other business priorities.
In the end, understanding and implementing resource scheduling transforms cloud cost management from a reactive headache into a real strategic advantage.
Why Scheduling Is Essential for Your Cloud Budget
Let's be blunt: putting resource scheduling in place isn't just a technical tweak. It's a core business strategy that directly impacts your company's financial health in the cloud. Every hour of scheduled downtime is an hour you don't pay for, turning a wild, unpredictable expense into something you can actually control. It's the difference between passively accepting your cloud bill and actively managing it.

The quickest, most dramatic savings almost always come from your non-production environments. Think about all those development, testing, staging, and QA instances. Their usage is incredibly predictable: they're needed during business hours, and that's about it. The rest of the time, they sit completely idle, burning cash through nights and weekends.
For a typical work week, that idle time adds up fast. We're talking over 120 hours where you're paying for infrastructure that is doing absolutely nothing. A simple schedule that powers these resources down when nobody's working stops this waste cold. If you want to see just how much this adds up, check out our deep dive on the hidden cost of idle VMs.
The Ripple Effect of Smart Scheduling
The benefits go way beyond the immediate financial wins. Resource scheduling creates a cascade of positive effects across the whole organization, reinforcing good cloud habits and strengthening your operational posture.
For starters, when you schedule a resource to be off, you're shrinking your digital footprint. An inactive server can't be targeted by an attacker. This simple practice reduces your company's attack surface and provides a straightforward, effective boost to security.
It also cultivates a culture of accountability. When teams have to justify why a particular resource needs to run 24/7, it forces more thoughtful planning. This kind of governance is critical for preventing the uncontrolled resource sprawl that secretly inflates your cloud bill.
By scheduling non-production environments, you establish a powerful default. Instead of resources running forever unless someone remembers to shut them off, they are off by default unless a specific need justifies keeping them on.
Practical Scenarios and Tangible Savings
Let's put some real numbers to this. Imagine a mid-sized company running ten development servers, each costing around $300 per month to run around the clock. Without any scheduling, the annual bill for just this small environment is a hefty $36,000.
Now, let's apply a basic schedule that powers these servers off during nights and weekends. This simple change can cut their runtime by roughly 70%. The financial impact is immediate.
- Annual cost without scheduling: $36,000
- Annual savings with scheduling (70%): $25,200
- New annual cost: $10,800
Just one policy change reclaims over $25,000 in wasted cloud spend every single year. Scale this across dozens or even hundreds of non-production resources, and you can see how the financial impact becomes truly significant. Resource scheduling is one of the fastest ways to prove the value of your FinOps and cloud cost management efforts.
Exploring Different Scheduling Models
Resource scheduling isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. The right approach depends entirely on your workload's predictability and purpose, and matching the right model to each environment is the key to unlocking major savings without disrupting your team's workflow. This means moving beyond a single, rigid strategy and adopting a more flexible mindset.
Different workloads simply demand different levels of availability. A development server, for example, has completely different uptime requirements than a customer-facing application. Once you understand these distinctions, you can apply the most effective and cost-efficient model for each specific use case.
Stop and Start Schedules
The most common and straightforward model is the stop and start schedule, often called a "time-based" or "office hours" schedule. This approach is perfect for environments with highly predictable usage patterns, like development, testing, and staging resources that are only needed during standard business hours.
You simply define a power-on time (say, 8 AM Monday) and a power-off time (6 PM Friday). The resources automatically shut down for nights and weekends, which cuts out waste without anyone on your team having to lift a finger. This simple method alone can slash non-production costs by over 70%.
Time-Based Scaling
Sometimes, you know a spike in demand is coming. Time-based scaling is a proactive model designed for planned events like a product launch, a big marketing campaign, or a scheduled data processing job. Instead of keeping resources at peak capacity 24/7, you schedule them to scale up just before the event and scale back down right after.
For instance, you could configure your e-commerce site's servers to triple in capacity for the 48 hours of a Black Friday sale. This ensures you deliver a smooth customer experience during the rush but aren't overpaying for that extra muscle during quieter periods. This is a core consideration when deciding if you should use cloud-native instance scheduler tools or a more specialized platform.
The goal is to align your infrastructure's power with your business's rhythm. A static, always-on approach is just inefficient. Dynamic models adapt to your needs, ensuring you have exactly the resources you need, precisely when you need them.
Event-Driven Scheduling
For workloads that are sporadic and unpredictable, event-driven scheduling offers the highest level of efficiency. Instead of running on a fixed clock, resources are triggered to start by a specific event and shut down automatically once the task is complete. This model is ideal for CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, or data ingestion jobs.
Think about these common scenarios:
- CI/CD Pipelines: A new code commit to a repository automatically spins up a build server to compile and test the code. Once the job is done, the server shuts down.
- Data Processing: An incoming data file to a storage bucket triggers a virtual machine to start, process the data, and then terminate.
With this model, resources only exist for the exact duration they are needed, reducing their cost to the absolute minimum. It’s the ultimate "pay-for-what-you-use" strategy in action.
How To Implement Resource Scheduling
Once you’re sold on the benefits of resource scheduling, the big question is: how do you actually do it? The right approach really boils down to your team’s technical skills, how mature your cloud operations are, and the sheer scale of your environment.
Most organizations head down one of three paths, each with its own pros and cons. They range from basic, hands-on methods to fully automated, specialized solutions. Understanding the trade-offs is crucial for picking a strategy that actually saves you money without creating a new headache for your team.
The Manual Approach
The most straightforward way to get started is the manual approach. This is exactly what it sounds like: someone, a developer or an IT admin, logs into the cloud console to manually shut down resources at the end of the day and fire them back up in the morning.
While it costs nothing upfront and requires zero technical setup, this method is wildly inefficient and a magnet for human error.
People get busy, and people forget. A developer pulling a late night to fix a bug is probably not thinking about shutting down a test server. That single oversight can leave a resource burning cash all night and through the weekend. Relying on manual actions is simply not a scalable or reliable way to achieve consistent savings.
Native Cloud Provider Tools
Taking a step up from manual work, the major cloud providers offer their own scheduling tools. Think AWS Instance Scheduler, Azure Automation, and Google Cloud Scheduler. These are a huge improvement, letting you create automated stop/start schedules using scripts and configurations right inside your cloud account.
But there’s a catch: these tools are far from plug-and-play.
They often demand a heavy lift to set up, requiring you to write and manage complex scripts (in Python or PowerShell, for instance) and have a deep understanding of services like Lambda, IAM roles, and event triggers. You’re also on the hook for maintenance. When a cloud provider updates a service, your scripts might break, and it’s up to your team to fix them.
Native tools give you a ton of power and flexibility, but you're trading ease of use for it. The entire burden of building, deploying, and maintaining the scheduling logic falls squarely on your team's shoulders.
For a much deeper dive into how these tools stack up against dedicated platforms, check out our Cloud Toggle scheduling guide.
Dedicated Third-Party Platforms
Your third option is using a dedicated third-party platform, a tool purpose-built for one thing: making resource scheduling painless. These platforms offer intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that hide all the messy technical details. Instead of wrestling with code, your team can click a few buttons in a dashboard and have schedules running in minutes.
These tools often come packed with features that native solutions just don't offer out of the box:
- Multi-Cloud Management: Control schedules for AWS, Azure, and GCP all from one central hub.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Give teams scheduling permissions without handing over the keys to the entire cloud account.
- Easy Overrides: Let developers temporarily pause a schedule for urgent work with a single click.
- Centralized Visibility: Get a clear view of all schedules and potential savings across your entire organization.
This simple decision tree helps visualize when to use different scheduling models based on how predictable your workloads are.
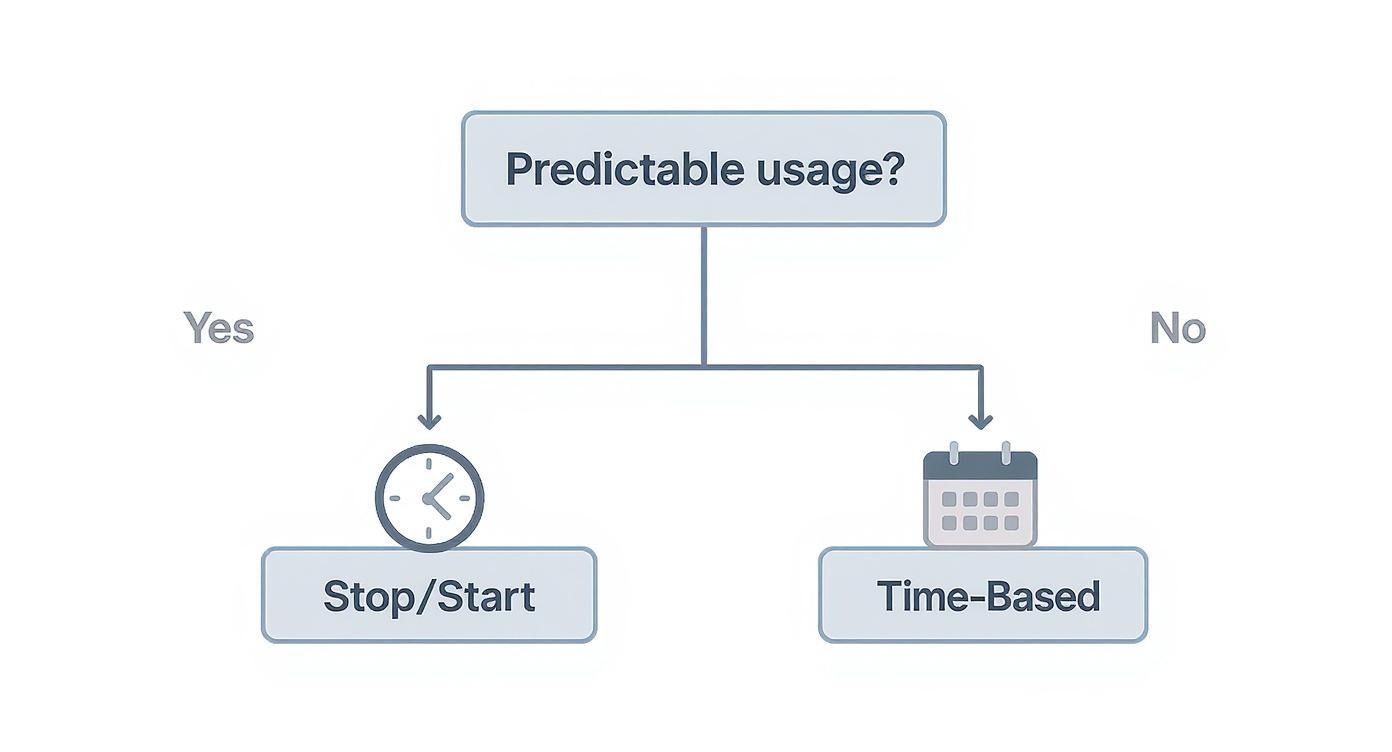
As the chart shows, if you know when a resource is needed, a simple stop/start schedule is perfect. If usage is more sporadic, a more dynamic approach is better. While you can build all of this with native tools and custom code, a third-party platform handles it for you, freeing your team to focus on building great products, not managing scheduling scripts.
Comparing Resource Scheduling Implementation Methods
Choosing the right implementation path depends entirely on your organization’s unique needs, resources, and priorities. This table breaks down the three main approaches to help you decide which is the best fit for your team.
| Method | Ease of Use | Initial Setup Effort | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual | Very Low | None | No cost or technical setup | Very small teams or one-off tasks where automation is overkill. |
| Native Cloud Tools | Low | High | High customization & control | Technically skilled teams with specific needs and the resources to manage complex scripts. |
| Third-Party Platforms | High | Very Low | Simplicity & rapid results | Teams that prioritize ease of use, multi-cloud management, and minimizing operational overhead. |
Ultimately, the goal is to find a solution that delivers maximum savings with the minimum amount of friction. Whether you build it yourself or buy a ready-made solution, the key is to move away from unreliable manual processes and embrace automation.
Best Practices for Effective Scheduling

To really unlock what resource scheduling can do, you need more than just a tool; you need a solid governance framework. Just turning things off is a decent start, but a real strategy is what delivers long-term savings without handcuffing your teams. It's all about striking that perfect balance between cost control and operational freedom.
The smartest way to begin? Go after the low-hanging fruit: non-production environments. Targeting your development, testing, and staging resources delivers immediate, high-impact savings with almost zero risk. This approach lets you score some quick wins and build momentum for a wider rollout.
Establish Clear Governance and Ownership
Before you push schedules out across the company, it's critical to define who's responsible for what. A clear, simple policy prevents confusion and makes sure schedules are actually managed, not just created.
First up, enforce a consistent resource tagging policy. Every single resource should have tags identifying its owner, project, and environment (like env:dev or project:phoenix). This simple step makes it incredibly easy to see which resources belong on which schedules and who to ping if there's an issue. Without tags, you're just flying blind.
You also need to set up automated alerts. Your team should get a notification the second a scheduled action fails, like a server that stubbornly refuses to shut down. This kind of proactive monitoring is key to maintaining a reliable scheduling system.
The most successful scheduling strategies are built on communication and flexibility. This isn't about restricting developers; it's about empowering them to be cost-conscious while giving them what they need to get their work done without roadblocks.
Implement Overrides and Regular Audits
A rigid, unchangeable schedule is a recipe for developer frustration. We all know that engineers sometimes need to work late to squash a critical bug or meet a tight deadline. That’s why a flexible override mechanism is completely non-negotiable.
An override lets a developer temporarily pause a schedule, keeping a resource running for an urgent task. This feature is absolutely crucial for getting buy-in from your engineering teams. It gives them the control they need without derailing the entire cost-saving effort.
Finally, remember that schedules aren't "set it and forget it." You have to audit them regularly to make sure they still make sense for the business.
- Quarterly Reviews: Do the schedules still line up with team working hours and project timelines? People's habits change.
- Prevent Drift: Make sure new resources are actually being added to schedules instead of being left to run 24/7. This is a classic source of cost creep.
- Optimize Performance: Look at usage patterns. Can you tighten some schedules for even more savings without impacting productivity?
By combining these practices, you'll build a tough, effective scheduling framework that delivers consistent savings while actually supporting your team’s workflow.
Your Top Scheduling Questions, Answered
As you start thinking about how resource scheduling could work for your team, a few practical questions always come up. Let's tackle the most common ones head-on so you can move forward with a clear strategy.
How Much Can You Really Save?
The savings are almost always bigger than people expect, typically ranging from 30% to over 70% on non-production cloud bills. Where you land in that range just depends on how many idle resources you have running when nobody's using them.
Think about a typical development environment. It’s probably only needed during the workday, right? That means it could be turned off for the other 120+ hours every single week. Just by doing that, you cut the cost of that one resource by nearly 75%. Now, multiply that across all your dev, test, and staging environments. The numbers add up fast.
Is It Safe to Schedule Production Resources?
You're right to be cautious here. Applying aggressive on/off schedules to production workloads is rarely a good idea since they need to be available 24/7 for your customers. But that doesn't mean you can't apply the same cost-saving principles to production.
The key is auto-scaling. Instead of a fixed schedule, auto-scaling automatically adds or removes capacity based on real-time traffic and demand. This ensures you have all the power you need for peak hours without overpaying for resources that sit idle during quieter periods. It’s scheduling, just driven by demand instead of a clock.
The biggest challenge is often cultural, not technical. It requires changing the default behavior of letting resources run indefinitely. Overcoming this involves clear communication about the financial benefits and providing teams with easy-to-use tools.
What's the Biggest Hurdle When Getting Started?
Honestly, the technology is the easy part. The real challenge is shifting the company culture away from the "always on" default. For years, the easiest thing to do was just leave everything running. Changing that habit is the biggest step.
Success hinges on getting your development and engineering teams on board. You can't just enforce new rules from the top down. The best way to do this is by showing them the direct impact on the budget and, crucially, giving them simple tools that don't get in their way. If they have an easy way to override a schedule for late-night work or an urgent deployment, they’ll embrace the change. It's about empowering them to be part of the solution, not restricting them.
Ready to stop wasting money on idle cloud resources? CLOUD TOGGLE makes it easy to automate your savings with intuitive, powerful scheduling tools. See how much you can save by starting a free trial today. Learn more at https://cloudtoggle.com.




