In the world of cloud computing, elasticity is the secret sauce that lets a system automatically grow or shrink its resources, things like servers, memory, or raw processing power, to perfectly match what’s needed in real time.
Think of it as a smart, self-adjusting system that never wastes money on resources you don't need or fails because you don't have enough.
What Does Cloud Elasticity Actually Look Like?
Imagine you run an e-commerce website. It's Black Friday, and your traffic suddenly explodes, jumping from a few hundred users to tens of thousands in just a few minutes.
Without elasticity, your website would crash under the pressure, leading to a flood of frustrated customers and lost sales. But with an elastic cloud setup, the environment instantly senses the surge and spins up more servers to handle the load.
Just as important, once the sale is over and traffic dies down, elasticity automatically scales everything back down. This is the core of what makes elasticity so powerful: you only pay for that peak capacity precisely when you needed it.
The Financial Power of Adapting in Real Time
The biggest win here is massive cost efficiency. You’re no longer stuck in the classic IT dilemma: either over-provision servers and waste money "just in case," or under-provision and risk a system meltdown.
Elasticity flips your IT spending from a fixed, upfront cost to a flexible, operational one. It perfectly aligns what you spend with what you actually use, cutting out the waste from idle resources and maximizing the financial upside of the cloud.
This responsive model is why the market is exploding. The global elastic computing market is on track to hit an incredible USD 1.24 trillion by 2028, proving just how vital it is for modern businesses. This trend shows a clear shift away from rigid, static infrastructure toward dynamic, on-demand models. You can dive deeper into this growth on the buzzclan.com blog about the elastic computing market.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Elasticity at a Glance
So, what are the fundamental ingredients of elasticity? It really boils down to a few core attributes working together to deliver both top-notch performance and financial smarts. Understanding these is the first step to building a truly cost-effective cloud environment.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation | Resources are scaled up or down based on predefined rules and metrics, all without needing a human touch. |
| Real-Time Speed | Adjustments happen in minutes or even seconds, ensuring the system can handle sudden, unexpected demand. |
| Pay-Per-Use | You're only billed for the computing resources you are actively consuming at any given moment. Nothing more. |
These characteristics make elasticity a cornerstone of modern cloud architecture. At the heart of it all are technologies like virtualization, which make this dynamic allocation possible. Exploring the pros of virtualization can give you a clearer picture of how these foundational technologies enable the cost savings and flexibility we see today.
Understanding Elasticity vs Scalability
It’s incredibly common to hear people use elasticity and scalability interchangeably. But in the real world of cloud computing, they solve very different problems on completely different timelines. Getting them mixed up can lead straight to a cloud strategy that’s either way too expensive or too fragile to handle actual demand.
The key difference really boils down to purpose and timing.
Think of scalability as your long-term, strategic plan for growth. It’s like an architect designing a restaurant with a solid foundation, knowing they can add a whole new dining wing next year without tearing everything down. You’re building the system with the capacity to handle future, sustained increases in demand. This is all about preparing for predictable, long-term expansion.
Elasticity, on the other hand, is your short-term, tactical response to what’s happening right now. For that same restaurant, it’s like adding extra tables and calling in more staff just for a chaotic Friday night dinner rush, then sending them home when things quiet down. It’s an automated, real-time reaction to unpredictable spikes and dips in traffic.
Elasticity vs Scalability Compared
To really nail down the difference, it helps to put them side-by-side. Each one plays a unique role in creating a cloud environment that's both resilient and cost-effective.
| Aspect | Elasticity | Scalability |
|---|---|---|
| Timeframe | Short-term (minutes/hours) | Long-term (months/years) |
| Driver | Reactive (responds to current demand) | Proactive (plans for future growth) |
| Automation | Almost always automated | Often involves manual planning and design |
| Goal | Match resources to demand precisely | Increase the overall capacity ceiling |
| Analogy | Adding temporary tables for a rush | Building a new wing for the restaurant |
This comparison makes it clear: elasticity is about efficiency and reacting to the moment, while scalability is about growth and future-proofing your architecture.
The core idea of elasticity is beautifully simple. It's built on three pillars: being automatic, on-demand, and pay-as-you-go.

This visual really drives home how elasticity combines automation with on-demand resource provisioning under a consumption-based billing model. It’s a powerful trio for efficiency.
A truly well-designed cloud system needs both. It must be scalable enough to handle business growth over the next quarter, yet elastic enough to survive an unexpected traffic surge this afternoon. Neglecting one for the other leaves you vulnerable to either performance failures or excessive costs.
Ultimately, your business needs a strategy that accounts for planned growth (scalability) while also managing unpredictable daily fluctuations (elasticity). You can dive deeper into the nuts and bolts by exploring how scaling works in our detailed guide. Getting this dual approach right is fundamental to building a powerful and financially sound cloud environment that can adapt to anything.
How to Implement Elasticity in Your Cloud Environment

Knowing what cloud elasticity is gets you halfway there. The real value comes from putting it into practice. Moving from theory to action means picking the right pattern for your specific needs, and thankfully, cloud providers have built some powerful, automated tools to help you do just that.
There are three main ways to build elasticity into your infrastructure. Each one is a great fit for different kinds of workloads, and choosing the right one ensures your applications are both responsive and cost-effective.
Autoscaling for Dynamic Workloads
Autoscaling is the go-to method for achieving true elasticity. It works by automatically adjusting the number of compute resources, like virtual machines or containers, based on rules and real-time performance metrics you set.
Imagine an e-commerce site running a Black Friday sale. With autoscaling, you can create a rule that says, "If the average CPU utilization across my servers climbs above 70%, spin up more servers." Just as important, you can set another rule: "If CPU utilization drops below 30% for ten straight minutes, start shutting servers down."
This dynamic, rule-based approach makes sure your application can handle surprise traffic spikes without anyone having to lift a finger. A great way to do this is with efficient VM auto scaling, which perfectly matches resources to demand, preventing both performance headaches and paying for idle capacity.
Serverless Computing for Event-Driven Tasks
Another fantastic way to implement elasticity is with serverless computing. Using services like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions, you stop managing servers entirely. You just upload your code, and the cloud provider runs it automatically in response to specific events or triggers.
The model is elastic by its very nature. Resources are spun up only for the milliseconds your code is executing and are gone the moment it’s done. You only pay for the exact compute time you use.
Here are a few common spots where serverless shines:
- Image Processing: A function can trigger every time a user uploads a photo, instantly resizing it or adding a watermark.
- Data Processing: A function can run whenever a new file lands in a storage bucket to process its contents.
- API Backends: Serverless functions are perfect for powering APIs, scaling from zero to thousands of requests in an instant with no pre-provisioned servers.
Scheduled Scaling for Predictable Patterns
Finally, scheduled scaling is a proactive approach that’s perfect for workloads with predictable peaks and valleys. Instead of reacting to performance metrics, this method adds or removes resources based on a fixed schedule. It’s the ideal solution for any environment that doesn't need to be running 24/7.
The classic example is a development or testing environment. If your team works 9-to-5, Monday to Friday, why pay for those servers to run all night and over the weekend? With scheduled scaling, you can automatically start them every weekday morning and shut them down every evening.
This simple practice guarantees cost savings by eliminating spend on completely idle resources. It perfectly complements reactive autoscaling by targeting the predictable waste that metric-based systems often miss.
Choosing the right implementation, or even a mix of them, is key. For teams wanting to go deeper, you can learn more about autoscaling in Kubernetes in our detailed post. When you match the elasticity pattern to your workload, you unlock the full financial and performance benefits of the cloud.
The Hidden Cost of Idle Cloud Resources
The biggest selling point of the cloud has always been simple: pay only for what you use. But if you look closely at your monthly bill, you'll likely find the ghost of idle resources haunting your bottom line. This waste quietly inflates your spending, chipping away at the very cost efficiency you were promised.
This problem is especially painful in non-production environments. Think about your development, staging, and quality assurance (QA) servers. They’re absolutely essential during the workday, but what happens at 5 PM? Or on a Saturday? They often sit completely idle, burning cash for no good reason. For any growing business, that's a significant and unnecessary financial drain.
Elasticity is the direct answer to this problem. It’s the mechanism that automatically powers down non-essential resources during predictable lulls, cutting waste right out of your cloud bill.
This isn’t just about trimming a few dollars here and there. It’s about building financial discipline into your cloud operations and making sure you’re getting the absolute most out of your investment.
The Scale of Cloud Adoption and Its Cost Challenges
Moving to the cloud isn't a trend anymore; it's just how business is done. By 2026, a staggering 95% of new digital workloads are expected to be built on cloud-native platforms, a huge leap from just 30% in 2021. And with over 78% of organizations already using multiple cloud providers, managing costs has become a real headache.
This explosion in adoption has created new challenges. Trying to manually enforce cost controls across different clouds and dozens of environments is nearly impossible. You can dig deeper into these trends with cloud computing statistics from Softjourn.
Why Elasticity Is the Answer to Idle Waste
To truly understand what is elasticity in cloud computing, you have to see it as a tool to fight this exact kind of waste. Real elasticity isn’t just about automatically scaling up for a traffic spike; it’s also about proactively scaling down to zero during predictable quiet periods.
Here’s where it makes a real-world impact:
- Development Environments: Why on earth would you pay for servers to run while your developers are asleep? Elasticity, especially through scheduling, makes sure they’re only running during business hours.
- Testing and QA Servers: These environments get hammered right before a release, but they might sit completely untouched for days or weeks afterward. Shutting them down automatically can save a small fortune.
- Demonstration Sandboxes: Sales or demo environments are only needed when you're showing them to a client. Keeping them off by default and firing them up on demand is a simple, incredibly effective cost-control measure.
By applying elastic principles to these predictable workloads, businesses can stop paying for infrastructure that isn't doing any work. This transforms elasticity from a technical feature into a powerful financial strategy, letting you align your spending precisely with your actual usage and finally capture the full economic promise of the cloud.
Maximizing Savings with Scheduled Elasticity

Autoscaling is a rockstar for handling unexpected demand, but it has one major blind spot: predictable, recurring idle time. It’s built to react to performance metrics, not your team’s work schedule. This is where scheduled elasticity comes in as your best financial ally, offering a proactive way to slash waste that autoscaling simply isn't designed to catch.
Scheduled elasticity hones in on resources with known usage patterns. The most obvious example is development and staging servers. Your engineering team needs them running from 9 AM to 5 PM, but what about the other 16 hours a day, plus weekends? They often sit completely idle, burning through your budget.
This proactive approach is the perfect partner to reactive autoscaling. By setting simple on/off schedules, you can guarantee savings without any complex engineering or finicky metric tuning. For any business trying to truly master what is elasticity in cloud computing, combining both methods is the key to a complete cost optimization strategy.
The Power of Predictable Shutdowns
The real beauty of scheduled elasticity is its simplicity and certainty. Instead of waiting for a metric like CPU usage to dip low enough, you just tell your resources exactly when to be on and when to be off. This is a game-changer for any non-production environment.
Common use cases are a great way to see the impact:
- Development and QA Environments: Automatically fire these up at the start of the workday and shut them down at the end. Just like that, you can save over 60% on their costs.
- Demonstration Sandboxes: Keep these costly demo environments off by default and only turn them on for scheduled client presentations.
- Batch Processing Jobs: Schedule resource-heavy jobs to run during off-peak hours when cloud costs are often much lower.
This simple shift turns cloud cost management from a reactive guessing game into a predictable, automated process. You're no longer hoping to save money; you are guaranteeing it by targeting the single largest source of waste, predictable idle time.
Simplifying Scheduling and Security
Sure, the big cloud providers offer their own native scheduling tools, but they can be a real headache to configure. Worse, they often require you to grant users excessive permissions across your account. This is a huge security risk. Do you really want to give a project manager or developer broad administrative access just so they can manage one server's schedule?
Platforms like CLOUD TOGGLE solve this problem by offering a simple, secure interface built for one thing: scheduling. You can safely delegate control to team members to manage their own environments without ever exposing sensitive infrastructure settings. It’s the best of both worlds, developers get the control they need, and you maintain tight security.
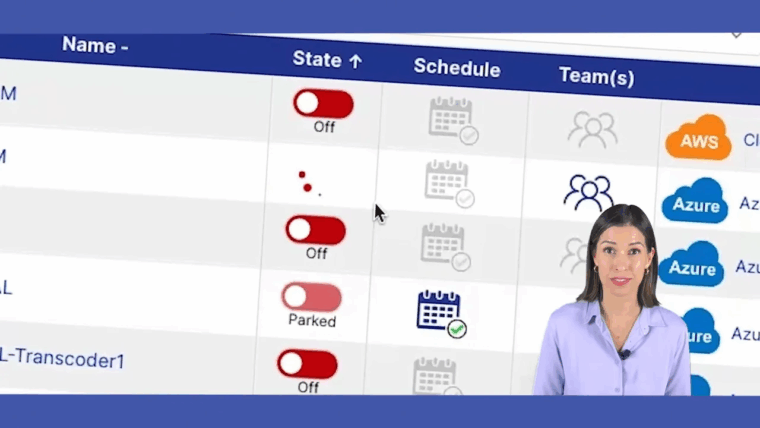
The screenshot below shows a clean, user-friendly dashboard for managing resource schedules.

This intuitive layout makes it easy for anyone on the team, not just cloud experts, to set and override schedules. It ensures resources are only active when needed. If you want a deeper dive, our CLOUD TOGGLE scheduling guide provides a detailed walkthrough. For growing teams, this blend of easy management and secure, delegated access is a powerful way to cut costs and make everyone’s job a little easier.
Cloud Elasticity: Your Questions Answered
Getting a handle on cloud elasticity brings up some common, practical questions. Whether you're a business owner trying to budget, a developer building an application, or an IT manager tasked with efficiency, the details matter. Let’s clear up a few of the most frequent ones.
What Are the Main Benefits of Cloud Elasticity for a Small Business?
For a small business, it boils down to two huge wins: massive cost savings and rock-solid performance. Elasticity stops you from over-provisioning, and overpaying for, infrastructure you don't need. You only pay for what you actually use.
When your website gets a sudden flood of visitors, an elastic system automatically adds resources to handle the load, preventing crashes and keeping customers happy. Once things quiet down, it scales back down, saving you money. This "pay-as-you-go" approach lets SMBs go toe-to-toe with larger companies without a crippling upfront investment in hardware.
Can Cloud Elasticity Ever Increase My Costs Unexpectedly?
Absolutely, if it isn't configured correctly. This is a common pitfall. Poorly set up autoscaling rules can cause your resources to scale up way too aggressively and, even worse, fail to scale down quickly after the traffic spike is over. The result? A much bigger bill than you were expecting.
That’s why getting your thresholds and cooldown periods right is so important. It's also why relying only on autoscaling for non-production environments is a mistake. Using a scheduling tool for your dev or staging servers guarantees they’re turned off overnight and on weekends, giving you predictable savings that reactive autoscaling just can't deliver.
How Do I Choose Between Autoscaling and Scheduled Scaling?
Good news, you don't have to choose. They solve different problems and work brilliantly together. Think of them as two different tools for two different jobs.
Use autoscaling for your live, production workloads where traffic is unpredictable. It’s built to react in real-time to keep your application available no matter what.
Use scheduled scaling for environments with predictable schedules, like development and testing servers that are only needed from 9 to 5. A dedicated tool is perfect here, letting you set simple "on/off" schedules that automatically and reliably wipe out wasted spend on idle resources.
Combining reactive autoscaling for production and proactive scheduling for non-production gives you a complete cloud cost optimization strategy. This two-pronged approach tackles both unpredictable demand and predictable waste, ensuring you aren’t overspending in any scenario.
Is It Difficult to Set up Elasticity in AWS or Azure?
For someone with solid cloud experience, setting up basic autoscaling in major platforms like AWS or Azure is fairly straightforward. The real challenge comes with fine-tuning the rules and managing all those policies across different teams and projects. That’s where things get complex and demand deep technical expertise.
This is where specialized platforms come in, particularly for scheduled elasticity. A simple, user-friendly interface lets you manage schedules across multiple clouds without needing to hand out full account access to everyone. It makes cost savings accessible to non-engineers and tightens up your organization's security at the same time.
Ready to stop paying for idle cloud resources and start maximizing your savings? CLOUD TOGGLE makes it easy to implement scheduled elasticity with a simple, secure platform. Start your free trial and see how much you can save by visiting https://cloudtoggle.com.