Cloud infrastructure management is all about how you oversee and control everything humming along in your cloud environment—think compute, storage, and networking resources. It’s the art and science of making sure your applications run smoothly, stay secure, and don't break the bank, all without having to touch a single piece of physical hardware.
What Is Cloud Infrastructure Management and Why Does It Matter

Think of cloud infrastructure management less like an IT task and more like the strategic command center for your entire digital operation. It's a huge leap from just launching a virtual server. We're talking about the ongoing discipline of optimizing, securing, and governing the very resources that power your business.
This is a world away from the old days of managing servers stacked in a rack or tucked away in a closet down the hall.
Instead of plugging in cables, you’re orchestrating a global fleet of virtual resources. That kind of power brings incredible agility, letting you scale up or down in minutes. But with great power comes great responsibility, and significant financial risk if you don't have a deliberate strategy in place.
The Core Goals of Cloud Management
Good cloud infrastructure management isn't just about keeping the lights on. It’s a practice laser-focused on hitting specific business goals that directly boost your bottom line and make operations run smoother.
The main objectives usually boil down to these four pillars:
- High Availability: Keeping your apps and services online and accessible around the clock. Downtime is lost revenue, plain and simple.
- Robust Security: Building a fortress around your data and infrastructure to fend off unauthorized access and cyber threats. This is non-negotiable for any organization.
- Seamless Scalability: Designing systems that can automatically grow or shrink with demand. Your performance should stay rock-solid, even during a massive traffic spike.
- Cost Optimization: Actively hunting down and eliminating wasted cloud spend to ensure you get the most bang for your buck.
To give you a clearer picture, here’s a quick breakdown of how these pillars translate into real-world business value.
Core Pillars of Cloud Infrastructure Management
This table summarizes the primary objectives of cloud management and connects them to tangible business outcomes, serving as a quick reference guide.
| Pillar | Objective | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Maximize uptime and prevent service disruptions. | Protects revenue, enhances customer trust, and maintains brand reputation. |
| Security | Protect data, applications, and infrastructure from threats. | Mitigates risk of data breaches, ensures regulatory compliance, and builds customer confidence. |
| Scalability | Ensure resources can dynamically adjust to workload demands. | Guarantees consistent performance, improves user experience, and supports business growth. |
| Cost Optimization | Eliminate waste and align spending with actual needs. | Reduces operational expenses, improves ROI, and frees up budget for innovation. |
Ultimately, a strong focus on these four areas transforms the cloud from a simple utility into a powerful, controlled asset.
A Rapidly Expanding Digital Foundation
The explosive growth of the cloud market tells you everything you need to know about why this matters. The cloud infrastructure services market is projected to surge from USD 158.89 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 493.41 billion by 2034.
This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental global shift. As more businesses rely on these on-demand resources, managing them effectively becomes absolutely critical. For a deeper dive into these foundational concepts, exploring comprehensive IT Infrastructure Management services can provide a broader context covering both cloud and on-premise setups.
At its heart, cloud infrastructure management is about transforming the cloud from a utility you consume into a strategic asset you control. It's the difference between merely using the cloud and using it well.
Without a solid management strategy, cloud environments can spiral into chaos and become incredibly expensive. Think of misconfigured resources, forgotten dev servers, and oversized VMs all quietly draining your budget. A structured approach turns that potential chaos into a well-oiled, efficient, and secure digital foundation for your business.
Understanding the Core Components of Cloud Infrastructure

To get a real handle on managing your cloud environment, you have to start with the fundamental building blocks. Imagine you're the architect of a digital city. Every city needs places for work to get done, warehouses to store goods, and a road network to connect everything.
Cloud infrastructure is no different. It all comes down to three core pillars: compute, storage, and networking.
Every single application, website, or service you run in the cloud is just a combination of these three things. Getting comfortable with how they work and interact is the first real step toward building a cloud setup that's cost-effective, secure, and performs the way you need it to.
Compute: The Digital Engine
Compute resources are the engines of your cloud infrastructure. They’re the brains of the operation, providing the processing power and memory your applications need to run calculations, execute tasks, and serve your users. Think of them as the factories and office buildings in your digital city where all the actual work happens.
In the world of cloud compute, you'll mainly run into two flavors:
- Virtual Machines (VMs): A VM, like an AWS EC2 instance, is basically an entire computer simulated in software. It gets its own operating system and a dedicated slice of resources, making it a perfect home for traditional applications that expect to live on a standalone server. VMs give you fantastic isolation and control.
- Containers: Managed by platforms like Docker and Kubernetes, containers are a much more lightweight approach. They package up an application and all its dependencies but share the host operating system. This makes them incredibly fast to launch and way more efficient for running modern, scalable applications built from many small "microservices."
The choice between VMs and containers isn't about which is better, it's about which is right for the job. A clunky legacy database might feel right at home on a VM, while that slick new web app is a prime candidate for containers.
Storage: The Infinite Filing Cabinet
Next up, your digital city needs somewhere to keep all its stuff. Cloud storage is your infinitely expandable, ultra-secure filing cabinet for every piece of data you own. But just like you wouldn't store family photos in a bank vault, not all data is the same. That's why cloud providers offer different storage types.
The two you’ll encounter most often are:
- Object Storage: This is like a massive, self-organizing warehouse for unstructured data. You store files, images, videos, and backups as individual "objects," each with its own unique ID. It’s unbelievably durable and cheap, making it perfect for massive amounts of data that you don’t need to access in a split second, like archives or data lakes.
- Block Storage: This acts more like a high-performance hard drive plugged directly into your compute instances. Data is stored in fixed-size "blocks," and it's built for speed. This is the go-to for performance-hungry applications like databases or any system that requires lightning-fast read/write operations.
Knowing the difference here is a classic cloud management win. It stops you from paying top dollar for high-performance storage when a cheaper, simpler option would have worked just fine.
Networking: The Secure Communication Lines
Finally, you need to connect all these pieces together. You also need to control how they talk to each other and, crucially, to the outside world. Cloud networking provides the secure "roads and highways" for your digital city, complete with toll booths, gates, and security guards.
One of the most important networking concepts is the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Think of this as your own private, fenced-off neighborhood within the larger public cloud. It’s a virtual network where you can launch your resources in total isolation, giving you complete control over your network layout, IP addresses, and security rules.
Tools like security groups and network access control lists act as your virtual firewalls, letting you create granular rules about what traffic is allowed in or out of your instances. As you build out your cloud strategy, understanding the difference between a Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud setup is critical, as these decisions fundamentally shape how you design and secure your network.
Automating Your Infrastructure with Infrastructure as Code
Manually configuring your cloud setup is a recipe for disaster. Clicking through web consoles to spin up servers or tweak network settings is painfully slow, riddled with human error, and nearly impossible to replicate perfectly every time. That old-school approach just can’t keep up with the demands of a modern business.
The answer is to treat your infrastructure just like you treat your application code. This is the core idea behind Infrastructure as Code (IaC), and it's a total game-changer for how we manage the cloud.

Instead of clicking around, IaC lets your team define and provision every single piece of your cloud environment using simple, human-readable code files. These files become the single source of truth, a blueprint that you can version, share, and run over and over again.
What Is Infrastructure as Code
Think of IaC like a detailed recipe for your entire cloud setup. This recipe lists every "ingredient" (your VMs, databases, networks) and gives precise instructions on how to put them all together.
Anyone on your team can follow this recipe and get the exact same result, every single time. It doesn't matter if it's for a development, staging, or production environment.
This brings some incredible advantages to the table:
- Consistency: Every environment built from the same IaC template is identical. This completely kills the frustrating "but it worked on my machine!" problem.
- Speed: Provisioning a complex environment becomes as simple as running a command. What used to take hours of manual work now takes minutes.
- Reduced Errors: By taking manual clicks and guesswork out of the equation, IaC slashes the risk of misconfigurations that lead to downtime or security holes.
- Collaboration: Infrastructure code can live in a version control system like Git. This means teams can collaborate on changes, review them, and track the entire history of their environment.
This level of automation is the bedrock of effective cloud infrastructure management, helping teams build reliable systems faster than ever. You can dive deeper by checking out the different cloud infrastructure automation tools available to make this happen.
Popular IaC Tools and Their Roles
A few powerful tools have popped up to make IaC a reality for teams of all sizes. While they all share the same philosophy, they have different ways of getting the job done.
The two most dominant players you'll run into are Terraform and AWS CloudFormation.
Terraform: This is an open-source, cloud-agnostic tool from HashiCorp. Its biggest selling point is its ability to manage infrastructure across different cloud providers, like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, and even on-premise resources, all from a single workflow.
AWS CloudFormation: As a native AWS service, this tool lets you model and provision your AWS resources using JSON or YAML templates. Because it's so tightly integrated with AWS, it gives you seamless control over Amazon's massive suite of services.
The sheer market dominance of the big cloud providers is what drives the adoption of these tools. AWS still leads the pack with 31% of the global market share, followed by Microsoft Azure at 25% and Google Cloud at 11%. Together, these three giants control over two-thirds of a market that pulled in a staggering US $106.9 billion in Q3 2025 alone, which shows you the massive scale these IaC tools are operating at.
Beyond Provisioning: Automation Patterns
IaC is the foundation, but a truly great automation strategy goes much further. Smart cloud management also leans on dynamic automation patterns that react to events in real-time, without a human ever having to step in.
Here are a couple of key patterns:
- Auto-Scaling: This is the cloud's real superpower. Auto-scaling automatically adds or removes compute resources based on what's happening right now, like a sudden traffic spike or a heavy processing job. Your application stays snappy and responsive, and you stop paying for idle resources during quiet times.
- Self-Healing Systems: These systems are built to detect and fix failures on their own. If a virtual machine crashes or becomes unresponsive, a self-healing system can automatically terminate the faulty instance and launch a healthy replacement, often before any of your users even notice something was wrong.
These patterns shift your team from a reactive to a proactive mindset. Instead of constantly putting out fires, you build systems that anticipate and handle problems on their own. This creates more stability and frees up your engineers to focus on building what's next.
Actionable Strategies for Cloud Cost Optimization
Cloud spending can feel like a runaway train. The same flexibility that makes the cloud so powerful also makes it easy to lose your grip on the budget. Without a clear game plan, companies often find themselves paying for resources they aren't even using, turning a brilliant asset into a serious financial drain.
This isn't a small-time issue. In fact, just trying to manage cloud spend is the single biggest challenge for 82% of IT leaders. With companies dropping $270 billion on infrastructure services in 2023, and the market projected to hit $947.3 billion by 2026, every wasted dollar counts. The main culprit? Idle resources, a silent budget killer in a world where 60% of business data now lives in the cloud.
So, let's move past the generic advice and dig into some battle-tested strategies that deliver real, measurable savings.
Start with Right-Sizing Your Resources
One of the quickest wins in cloud cost optimization is right-sizing. It’s all about matching your instance types and sizes to what your application actually needs, not what you think it might need someday. It's incredibly common for teams to overprovision resources "just in case," leading to a ton of waste.
For instance, a development server might be running on a machine with far more CPU and memory than it requires. By looking at performance metrics over a few weeks, you can often downgrade to a smaller, cheaper instance without anyone noticing a difference in performance. This simple audit can lead to massive savings across your entire infrastructure.
Eliminate Waste from Idle Resources
The biggest source of hidden costs is almost always idle resources, especially in non-production environments like development, testing, and staging. These environments are the lifeblood of innovation, but they absolutely do not need to be running 24/7.
Think about a typical workday. Your development team is online from roughly 9 AM to 5 PM, Monday through Friday. That adds up to about 40 hours per week. But a full week has 168 hours.
This means your non-production servers are sitting completely idle for over 75% of the time, every weeknight and the entire weekend, yet you're paying for every single second. This wasted spend offers zero value to your business.
This is where resource scheduling becomes a total game-changer. By automatically powering down these servers during off-hours, you can immediately stop paying for resources that nobody is using.
Implement Automated Resource Scheduling
Resource scheduling is simply the practice of automatically starting and stopping your virtual machines and other cloud resources based on a schedule you set. It's a simple concept with a massive impact on your monthly bill. Instead of nagging engineers to manually shut things down, automation ensures it happens like clockwork.
Here’s how you can get this strategy rolling:
- Identify Your Targets: Start with the low-hanging fruit: non-production environments. Your development, staging, and QA servers are perfect candidates.
- Define Your Schedules: Create schedules that mirror your team's working hours. A common setup is to run servers from 8 AM to 6 PM on weekdays and shut them down completely on weekends.
- Use an Automation Tool: While cloud providers have native tools, they can be a headache to configure. A platform like CLOUD TOGGLE gives you a simple, point-and-click interface for creating and managing these schedules without needing to be a cloud guru.
Automating this process removes the risk of human error and guarantees savings. For a more detailed look at the financial impact, our guide on reducing the cost of your AWS and Azure infrastructure offers some great practical examples.
Leverage Reserved Instances for Predictable Workloads
For your production workloads that run predictably around the clock, Reserved Instances (RIs) or Savings Plans offer another powerful way to save. By committing to a one- or three-year term for specific instance types with providers like AWS or Microsoft Azure, you can lock in a significant discount compared to on-demand pricing.
This strategy is ideal for your stable, long-term applications, like your main production database or core app servers. The key is to analyze your usage patterns to pinpoint which resources have consistent uptime, making them safe bets for a long-term commitment.
Comparing Cost Optimization Strategies
To pull it all together, not all cost-saving methods are created equal. Some offer quick wins with minimal effort, while others require more planning for a bigger payoff. This table breaks down the most common strategies to help you decide where to focus first.
| Strategy | Impact Level | Implementation Complexity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Scheduling | High | Low | Non-production (dev, test, staging) environments with clear on/off hours. |
| Right-Sizing | Medium | Medium | Overprovisioned instances where usage data shows a smaller size will suffice. |
| Reserved Instances (RIs) | High | Medium | Stable, predictable production workloads that run 24/7. |
| Deleting Unused Resources | Varies | Low | Orphaned storage volumes, old snapshots, and forgotten test VMs. |
Ultimately, a truly effective cost optimization plan isn't about choosing just one of these. The best approach is a blended one: use Reserved Instances for your always-on production workloads and automated scheduling for everything else. This combination ensures you're never paying for more than you absolutely need.
Choosing the Right Cloud Management Tools
Navigating the world of cloud management tools often feels like a choice between two extremes: the raw power of native solutions and the focused simplicity of specialized platforms. When it comes to a high-impact task like scheduling your virtual machines on and off, this decision becomes even more critical.
Your choice directly impacts your cloud bill, your team's day-to-day efficiency, and your overall security posture.
On one side, you have the tools offered directly by the cloud giants. Solutions like AWS Instance Scheduler or Azure's Start/Stop VMs v2 feature are incredibly powerful and baked right into their ecosystems. They give you granular control, but only if you're comfortable scripting, wrestling with IAM roles, and navigating complex configurations.
But all that power comes with a steep learning curve. Native tools demand a serious investment in technical expertise and time just to get them running, let alone to maintain them. They simply weren't built for accessibility, which creates a huge hurdle for any team wanting to get non-engineers involved in saving money.
The Native Tooling Challenge
For most small and midsize businesses, the sheer complexity of native schedulers is a deal-breaker. Setting one up is never a simple point-and-click affair. You’re typically deploying pre-written code, meticulously configuring permissions, and needing a deep understanding of the services that make it all tick.
This technical barrier creates a bottleneck. If only a senior engineer can tweak a server's schedule, the entire process grinds to a halt.
Worse, it often forces you to grant broader infrastructure access than is truly necessary, opening the door to security risks. Handing over the keys to your entire cloud environment just so someone can manage a schedule is a security practice nobody recommends.
The core problem with native tools is that they solve the issue for the machine, but not for the people. A perfect script that no one can easily or safely use is far less effective than a simple, secure interface that the whole team can adopt.
This visual decision tree helps put these cost-saving strategies into context, showing how you move from reacting to high bills to proactively choosing between reserved instances and scheduling.
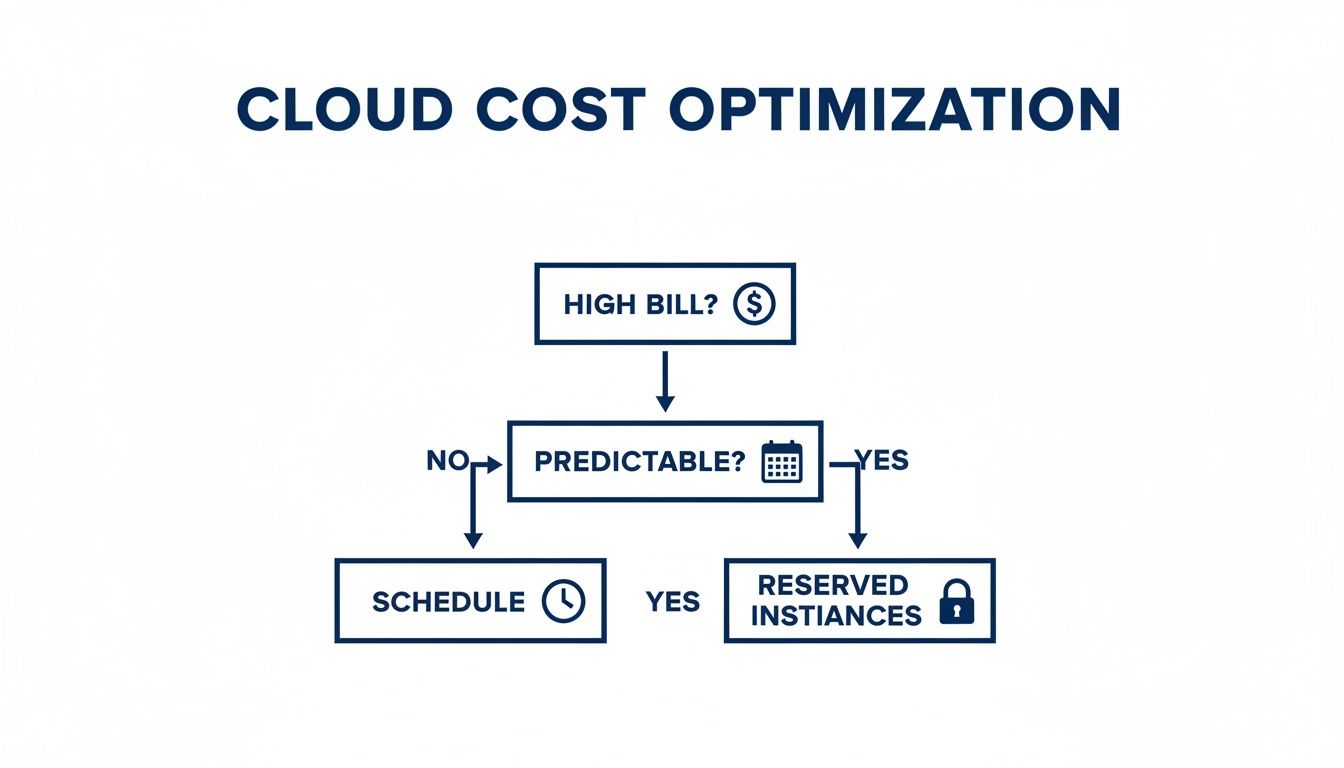
As the flowchart shows, when you're dealing with unpredictable workloads where reserved instances don't make sense, scheduling becomes your go-to strategy for controlling costs.
Prioritizing Simplicity and Security
This is exactly where a specialized platform like CLOUD TOGGLE shines. It was built from the ground up to do one thing exceptionally well: make resource scheduling simple, secure, and accessible to everyone. Instead of a complex technical setup, you get an intuitive interface that just works.
The real game-changer is the approach to access control. CLOUD TOGGLE uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) designed specifically for scheduling.
Here's what that means in practice:
- Empower non-technical staff: A project manager or someone from the finance team can safely adjust schedules for their projects without ever needing to log into the AWS or Azure console.
- Enforce the principle of least privilege: Users get access only to the scheduling functions they need. This drastically shrinks your security exposure compared to granting broad IAM permissions.
- Streamline governance: You get a clear audit trail showing who scheduled what and when, making cost allocation and accountability a breeze.
By focusing on a friendly user experience backed by rock-solid access controls, specialized tools make cost optimization a team sport. To see how this fits into the bigger picture, you can learn more about the benefits of a dedicated cloud management platform and how it anchors a wider strategy.
Ultimately, the right tool comes down to your team's reality. If you have dedicated cloud experts with the bandwidth to manage complex scripts, native tools are a perfectly viable option. But for most teams that value speed, security, and getting everyone involved in saving money, a dedicated solution offers a much clearer path to success.
Got Questions About Cloud Infrastructure Management?
So, you're diving into cloud infrastructure management and, naturally, questions are popping up. It's a big topic with a lot of moving parts. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to give you a clearer picture and help you build a solid strategy.
What Is the Biggest Challenge in Cloud Infrastructure Management?
Hands down, the biggest headache is cost management. The cloud's pay-as-you-go model is a classic double-edged sword. It gives you incredible flexibility, but it can also lead to a runaway budget if you’re not paying close attention.
It happens all the time. Teams overprovision resources "just in case" or, more commonly, forget to shut down development and testing environments over the weekend. This adds up, fast. In fact, industry data shows that managing cloud spend is the top priority for over 80% of organizations. Good cloud management means putting strict cost controls in place, constantly monitoring what's running, and using smart automation to keep the budget in line without slowing everyone down.
How Does Automation Improve Cloud Infrastructure Management?
Think of automation as the engine that powers modern cloud management. By using practices like Infrastructure as Code (IaC), you can create consistent, repeatable environments. This single change drastically cuts down on the human errors that inevitably creep in during manual deployments.
Automation also unlocks powerful patterns like auto-scaling, which lets your applications handle sudden traffic spikes without anyone on your team needing to jump in and manually add more servers. But maybe most importantly, automation is a huge driver of cost savings. It can systematically shut down idle resources during off-hours, turning a major source of waste into significant savings. Ultimately, it frees up your skilled engineers from repetitive, boring tasks so they can focus on what really matters: building new features and making your systems better.
Monitoring and observability are your eyes and ears in the cloud. They are essential for understanding not just what is happening with your infrastructure, but why it's happening, which is crucial for both performance tuning and cost control.
When Should I Use a Specialized Tool Instead of Native Schedulers?
You’ll want to reach for a specialized tool like CLOUD TOGGLE when your priorities are simplicity, security, and ease of use. Native schedulers from providers like AWS or Azure are definitely powerful, but they often come with a steep learning curve. Getting them right usually means writing custom scripts and wrestling with complex permission setups.
A specialized platform is perfect for teams who need something that just works, right out of the box. Its biggest advantage is providing secure, role-based access designed specifically for scheduling. This means non-engineers, like project managers or people from the finance team, can safely manage server uptime without needing access to your entire cloud infrastructure. It’s the right call for any organization that wants a straightforward, dedicated solution for cutting costs from idle resources.
What Is the Role of Monitoring in Cloud Management?
Monitoring and observability are the absolute foundation of good cloud infrastructure management. At a basic level, monitoring is about tracking key metrics, CPU usage, memory, network traffic, to make sure everything is healthy and running as it should.
Observability takes it a step further. It helps you understand why things are happening by connecting the dots between logs, traces, and metrics from all over your systems. In the real world, this combined visibility helps you do a few critical things:
- Find and fix performance bottlenecks before your users even notice.
- Troubleshoot issues much faster by getting straight to the root cause of a problem.
- Spot potential security threats by noticing unusual activity.
- Uncover cost-saving opportunities, like identifying those chronically underused VMs that can be downsized or shut off for good.
Without solid monitoring, you're essentially flying blind. It's impossible to properly optimize your environment for performance, security, or cost.
Ready to stop paying for idle cloud resources? CLOUD TOGGLE makes it easy to automate server schedules, reduce waste, and slash your AWS and Azure bills. Start your free 30-day trial and see how much you can save at https://cloudtoggle.com.