Deciding between AWS and Azure often boils down to your team's existing tech stack and long-term goals. If your organization is heavily invested in Microsoft tools, Azure offers a nearly seamless integration and excels at hybrid cloud setups, making it a natural fit for established enterprises. On the other hand, if you're building cloud-native apps from the ground up and value the largest service portfolio, AWS provides a mature, developer-focused platform that's hard to beat.
AWS vs Azure a High Level Comparison for Decision Makers

Choosing your cloud provider is a foundational move, especially for SMBs and DevOps teams where every dollar and developer-hour counts. This decision ripples through everything from your daily workflows to your monthly operational budget. This guide cuts through the noise of endless feature lists to give you a practical, high-level view of the AWS versus Azure landscape.
We'll focus on the core philosophies and strategic strengths of each platform. Getting these fundamentals right is the first step to ensuring your cloud provider aligns with your business objectives, technical capabilities, and future growth. From here, we can dive deeper into specific services, pricing models, and management tools.
Market Position and Core Philosophies
The cloud infrastructure market is largely a two-horse race, and while AWS has been the long-standing leader, Azure's aggressive growth makes this a critical decision for any cost-conscious business. As of Q3 2025, AWS maintains a commanding 29% global market share in cloud infrastructure services. However, Microsoft Azure has impressively captured 20% market share in the same period, signaling its rapid ascent in the enterprise space.
AWS built its empire on a developer-first, API-driven model, creating a vast and mature ecosystem of services. Azure, playing to its strengths, leverages Microsoft's dominance in the enterprise to deliver exceptional hybrid cloud solutions and a familiar environment for anyone already using Windows Server, Office 365, or other Microsoft products.
For a broader look at how these two giants are positioned, this high-level cloud platform comparison between AWS and Azure offers a great starting point, highlighting their different market approaches.
To help you see the key differences quickly, here's a side-by-side look at what defines each platform.
AWS vs Azure at a Glance
| Attribute | AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Azure (Microsoft Azure) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Unmatched breadth of services and market leadership. | Seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem. |
| Ideal User | Teams building cloud-native applications from scratch. | Enterprises with existing Microsoft investments. |
| Market Focus | Startups, developers, and public sector organizations. | Enterprise customers and hybrid cloud deployments. |
| PaaS vs IaaS | Stronger IaaS foundation with a massive service portfolio. | Strong PaaS offerings and excellent hybrid capabilities. |
This table provides a snapshot, but the best choice always depends on your specific needs, from the skills your team already has to the type of applications you plan to build.
Comparing Core Services for Compute, Storage, and Networking

When you're comparing AWS and Azure, you have to start with the big three: compute, storage, and networking. These are the absolute foundations of your cloud setup. For small businesses and DevOps teams, the small operational details in these core services can make a huge difference in performance, cost, and the headaches you deal with day-to-day.
It’s not enough to just look at a feature checklist. That won’t tell you which platform is actually a better fit for what you’re building. We need to dig into the real-world differences, like instance families, storage pricing quirks, and how complex it is to get your network running.
Compute: EC2 vs. Azure Virtual Machines
At the heart of it all is your compute engine. AWS has its famous Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), and Azure offers Virtual Machines (VMs). They do the same job, but how you use them and the options you get are surprisingly different.
AWS EC2 is the king of variety, with over 600 instance types built for everything from general use to memory-heavy or accelerated computing tasks. That level of detail is fantastic for dialing in performance perfectly, but it can also be overwhelming if you're a small team just trying to get a server running.
Azure, on the other hand, keeps things a bit simpler by grouping its VMs into series (like the burstable B-series or compute-focused F-series). This feels more familiar if you're used to traditional server sizing. Plus, if you're already a Microsoft shop, the Hybrid Benefit is a game-changer, letting you reuse existing Windows Server and SQL Server licenses to seriously cut costs.
A crucial difference I've seen in the trenches is how they handle spot instances. Both platforms sell off their spare capacity for huge discounts. But AWS Spot Instances are just more mature; they’re deeply integrated into so many other services, making them the default choice for things like CI/CD pipelines or big data processing. Azure's Spot VMs are great, but the ecosystem around them is still playing catch-up.
Here’s how they really stack up on the things that matter operationally.
| Feature | AWS EC2 | Azure Virtual Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Instance Variety | Massive selection lets you fine-tune performance down to the dollar. | Structured into series, making it easier for newcomers to choose. |
| Startup Times | Generally quicker to provision, especially for standard Linux images. | Can sometimes take a bit longer to get up and running. |
| Spot Market | A mature and dynamic market, perfect for cost-sensitive, fault-tolerant jobs. | Offers great savings but with a less volatile pricing model. |
| Windows Integration | Supports Windows perfectly, but you're paying for the license. | Seamless integration and real cost savings with the Azure Hybrid Benefit. |
Storage: S3 vs. Azure Blob Storage
Object storage is another non-negotiable. You’ll use it for everything from daily backups to hosting static assets for your website. AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) is the original and still the industry benchmark, with Azure Blob Storage as its main rival.
On the surface, they're nearly identical. Both have versioning, lifecycle rules to move data to cheaper tiers (like Hot vs. Archive), and solid security. The real devil is in the details of their pricing, especially around data transfer and API requests.
Data egress fees, what it costs to pull your data out of the cloud, can be a nasty surprise on your bill. While the sticker prices are similar, the final cost can swing wildly based on the region and how much data you’re moving. You absolutely have to model this out based on how your application actually behaves.
Networking: VPC vs. VNet
Finally, you need a secure, isolated space for all your resources to live. AWS provides this with Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and Azure calls its version Virtual Network (VNet). Functionally, they're two sides of the same coin. Both let you define your own private IP space, create subnets, manage route tables, and set up network gateways.
The key difference often boils down to the user experience. Many seasoned DevOps engineers I know prefer the raw power and flexibility of AWS VPC. You can control every little piece of your network, but that power comes with a much steeper learning curve.
Azure VNet, in contrast, gets a lot of praise for being more intuitive, particularly when you need to connect your on-premise datacenter to the cloud. This fits perfectly with Azure's strong focus on enterprise and hybrid cloud scenarios. Your choice here really comes down to a classic trade-off: do you want granular control, or do you want simplified management?
Evaluating Global Infrastructure and Regional Presence
When you're comparing AWS and Azure, the physical location of your data centers is a massive deal. It's not just a pin on a map. It directly hits your application performance, what your users experience, and whether you’re playing by local data laws. For any business with a global user base or serious disaster recovery needs, a provider’s footprint isn't a vanity metric; it’s a core strategic asset.
Looking past a simple count of "regions" is where the real analysis begins. The best choice often comes down to where your customers are and which international markets you’re trying to crack. A provider might boast about having more regions globally, but if they don't have a solid presence in a key market for your business, that advantage is totally meaningless to you.
Analyzing Data Center Networks
A cloud provider's global reach is all about reducing latency, the time it takes for your application to respond to a user. Lower latency means faster load times and a smoother experience, which can be the difference between a happy customer and a lost one. Both AWS and Azure have poured billions into building out huge, interconnected global networks, but they took slightly different paths to get there.
AWS got a head start and built a deep presence in major economic hubs. Azure, on the other hand, played catch-up with an aggressive expansion strategy, aiming to cover as many geographical and political boundaries as possible. That strategy has really paid off for them in terms of sheer regional availability.
The real differentiator isn't just the number of regions, but where they are. A data center in Frankfurt, for example, is non-negotiable for serving European customers while complying with GDPR. Likewise, a presence in Singapore is critical for tapping into the booming Southeast Asian market. Your decision has to be guided by your specific geographic targets.
Compliance and Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty, the idea that data is subject to the laws of the country where it’s located, is no longer a niche concern for lawyers. Regulations like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California have sharp teeth, imposing strict rules on how personal data is handled, stored, and moved.
Getting this wrong can lead to massive fines and a PR nightmare. Both AWS and Azure offer specific regions and services designed to help you meet these obligations. For instance, they both have dedicated government cloud environments that are physically and logically sealed off to handle sensitive public sector data.
When you compare AWS and Azure on global reach, Azure's vast network gives it a clear edge in total coverage. Microsoft Azure operates more than 400 data centers across over 70 regions. That gives it a much broader footprint than AWS, which has over 150 data centers in a similar number of regions. This massive infrastructure is a big reason why Azure is so strong in compliance-heavy industries.
The trick is to map your specific compliance requirements directly to what each provider offers in their available regions. You need to check their documented adherence to local laws. This is a crucial step that goes way beyond a simple tech spec comparison. Understanding the nuances of each provider's market share can also provide context. You can learn more about cloud provider market share in our detailed analysis.
Getting a Grip on Cloud Pricing and Cost Management Tools

Understanding cloud pricing isn't about memorizing a price list; it's about figuring out what your total bill will actually look like. At first glance, AWS and Azure seem to have similar pricing, but the devil is in the details. Hidden costs and management overhead can inflate your bill in ways you didn't expect, and for FinOps and IT teams, spotting these traps is the key to keeping your budget in check.
Both platforms give you the standard menu of pricing options: pay-as-you-go for flexibility, long-term commitments for discounts, and spot instances for huge savings on workloads that can be interrupted. But the real surprises often come from things like data egress fees, API call charges, and the cost of support plans. These can add up fast.
Core Pricing Models: A Direct Comparison
The bedrock of both AWS and Azure pricing is pay-as-you-go. This gives you maximum flexibility by charging you for resources by the second or minute. It’s perfect for development environments or any workload where demand is all over the place.
For your steady, predictable workloads, both providers will give you a break if you commit:
- AWS Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans can cut your costs by up to 72% if you commit to one or three years for specific instance types or overall compute usage.
- Azure Reserved VM Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans work in a very similar way, letting you lock in better rates for consistent workloads.
If you're really looking to slash costs, you can use their spare capacity. AWS Spot Instances and Azure Spot Virtual Machines can drop your compute costs by up to 90%. The catch? The provider can pull the plug with very little warning, so this is only for fault-tolerant stuff like batch processing or CI/CD pipelines.
Here’s where a lot of teams go wrong: they stick with pay-as-you-go for stable production workloads and end up overpaying every single month. A smart cloud strategy means constantly checking your usage and moving resources to the most cost-effective pricing model. It's not a "set it and forget it" deal.
Uncovering Hidden Cloud Costs
Beyond the obvious compute and storage costs, a few "hidden" fees often catch teams by surprise. Data egress fees, the cost to move data out of the cloud, are a big one. Pushing data in is usually free, but pulling it out to the internet or even to another region can get expensive quickly.
Other costs to watch out for include:
- API Calls: Charges for hitting services like storage or databases can stack up fast in chatty applications.
- Load Balancers and NAT Gateways: These are essential networking pieces, and they come with their own hourly and data processing fees.
- Premium Support Plans: Getting expert help isn't free. Support plans often cost a percentage of your total monthly spend, which can be a hefty sum.
To really get ahead of these costs, you need solid effective cloud governance strategies. This means setting up rules to control spending before it happens. For a deeper dive into how these costs stack up, check out our guide on the pricing differences between AWS vs Azure.
Native Cost Management Tools: AWS vs. Azure
Both AWS and Azure offer built-in tools to help you see where your money is going. AWS Cost Explorer gives you a detailed look at your historical and projected spending, while Azure Cost Management + Billing offers similar dashboards, budget alerts, and recommendations right inside the Azure portal.
The market itself shows why this matters more than ever. Azure is growing faster than AWS in percentage terms, a trend that's making engineering and FinOps leaders rethink their strategies. In 2025, Azure reported 33% year-over-year growth, pushing its market share to 23%. Meanwhile, AWS grew at a still-impressive 17.5-20% to hold its 29-30% lead. This fierce competition is nudging more companies toward multi-cloud setups to find the best price and avoid being locked into one provider.
While these native tools are a great first step for visibility, they often lack teeth when it comes to automation. They’re good at showing you where you're spending money, but they rely on you to manually go in and make changes. That operational overhead is exactly why many teams look to third-party solutions to automate cost optimization and turn insights into action without all the manual effort.
Native Cost Optimization Tool Comparison
While the built-in tools from AWS and Azure are useful for basic visibility, they have limitations when it comes to automated scheduling and proactive cost control. This is where dedicated third-party solutions often provide a much clearer ROI.
| Feature | AWS Instance Scheduler | Azure Start/Stop VMs v2 | Third-Party Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Complexity | High (requires CloudFormation/Lambda deployment) | Moderate (requires Logic App and Function setup) | Low (SaaS platform, minimal setup) |
| Multi-Cloud Support | No (AWS only) | No (Azure only) | Yes (Manages AWS, Azure, and others from one dashboard) |
| User Interface | None (managed via tags and config files) | Basic (managed through Logic App and tags) | Intuitive UI for creating schedules and managing permissions |
| Scheduling | Tag-based, requires specific syntax | Tag-based, less flexible scheduling logic | Visual calendar, team-based schedules, on-demand overrides |
| Cost | Free, but you pay for the underlying AWS resources | Free, but you pay for the underlying Azure resources | Subscription-based, but delivers direct savings far beyond cost |
As you can see, the native options are functional but clunky. They put the burden of setup and management squarely on your team. A dedicated solution simplifies the entire process, making it easy to implement schedules and start saving money right away.
How to Automate Cloud Cost Optimization
Once you've got a handle on your spending patterns, the next move is automation. Let's be honest, manually shutting down resources is a chore that's easy to forget, and it's just not scalable. Real, sustainable cost control comes from automatically powering down idle servers. It’s the single most effective way to stop wasting money without touching performance.
The real goldmine here is scheduling. Think about your non-production environments like development, staging, and QA. They often sit completely idle for more than half the day, burning cash every night and weekend. Automating their shutdown ensures you only pay for compute resources when your team is actually using them.
Implementing Smart Scheduling
Effective automation isn't just a clunky on/off switch. A truly useful platform gives you an intuitive scheduling interface that anyone on your team, technical or not, can use to manage server uptime. This breaks the bottleneck of relying on a busy DevOps engineer for every little change.
Here are the features that actually matter:
- Intuitive Visual Schedulers: No one wants to wrestle with JSON or YAML files just to turn off a server. A clean, calendar-style view makes setting and tweaking schedules dead simple.
- Instant Override Capabilities: A developer needs to burn the midnight oil or jump on during a weekend? They should be able to override a schedule in seconds without needing to file a ticket.
- Multi-Cloud Support: If you're running workloads in both AWS and Azure, managing everything from one unified dashboard is a massive operational win.
Secure Access for Non-Technical Users
One of the stickiest problems when you compare AWS and Azure cost management is figuring out how to delegate control safely. You can't just hand over admin keys to everyone, but you need their help to keep costs down.
This is exactly where dedicated scheduling platforms prove their worth. They add a secure, isolated layer that lets non-technical users manage schedules for their specific resources without ever needing to log into the AWS or Azure console. It empowers teams to own their costs while keeping your security and governance policies locked down.
By abstracting away all the underlying complexity, you start building a culture of cost awareness. Project managers and QA leads can easily adjust schedules for their own environments, making a direct impact on the budget. For a deeper dive, you can learn more about the role of automation in the cloud and its benefits.
Calculating the ROI of Automation
The financial upside of automated scheduling is immediate and surprisingly easy to calculate. Let’s walk through a very common scenario for a development team.
Example ROI Calculation:
- Resources: 10 general-purpose development servers.
- Cost: Each server runs about $0.20 per hour.
- Idle Time: Servers are only needed during an 8-hour workday, which means they're idle for 16 hours on weekdays and the full 48 hours over the weekend.
A good platform provides a clear dashboard showing your cloud connections and scheduled resources, making it simple to see the savings pile up.
This kind of visual interface puts you in control, letting you manage AWS and Azure environments side-by-side without flipping between native tools.
By scheduling these 10 servers to shut down when they're not needed, the savings add up fast. Turning them off for 16 hours each weekday plus the entire weekend cuts 560 hours of wasted compute time every single week. At $0.20 per hour, that’s $112 in weekly savings, or over $5,800 a year, from one simple rule. It’s a perfect example of how a small investment in the right automation tool delivers a huge and predictable return.
A Practical Framework for Making Your Decision
Choosing between AWS and Azure really comes down to lining up the platform’s strengths with your company’s unique DNA. This decision isn't just about the tech; it's about your team's skills, the software you already own, and where you want to go long-term. When you boil it all down, the choice gets a lot clearer.
For instance, if your team is building a brand-new, cloud-native application from the ground up, AWS is often the default choice. Its massive service catalog and developer-first tools give you incredible flexibility to innovate and scale. The platform's sheer maturity means there's a solution for almost any technical problem you can dream up.
On the other hand, if your organization is already running on Microsoft software, Azure offers a much more integrated path to the cloud. The seamless connection with tools like Office 365, Windows Server, and Active Directory simplifies management and can slash costs through programs like the Azure Hybrid Benefit.
Key Questions to Guide Your Choice
To make the right call, you need to get your key people in a room and walk through a few critical questions. The answers will point you in the right direction for your specific situation.
- Technical Skills: What cloud platforms does your engineering team already know? Sticking with what they're familiar with means faster development and less operational risk.
- Existing Infrastructure: Are you heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem? If you are, Azure’s native integration is a huge plus.
- Compliance Needs: Do you operate in a regulated industry like healthcare or finance? Check which provider has a stronger compliance game in your specific geographic regions.
- Budget Priorities: Is your main goal maximum flexibility with pay-as-you-go pricing, or are you looking for predictable costs through long-term commitments and existing license discounts?
This decision tree helps visualize that core logic. It guides you from your primary goal to the most logical platform choice and underscores the universal need for solid cost management.
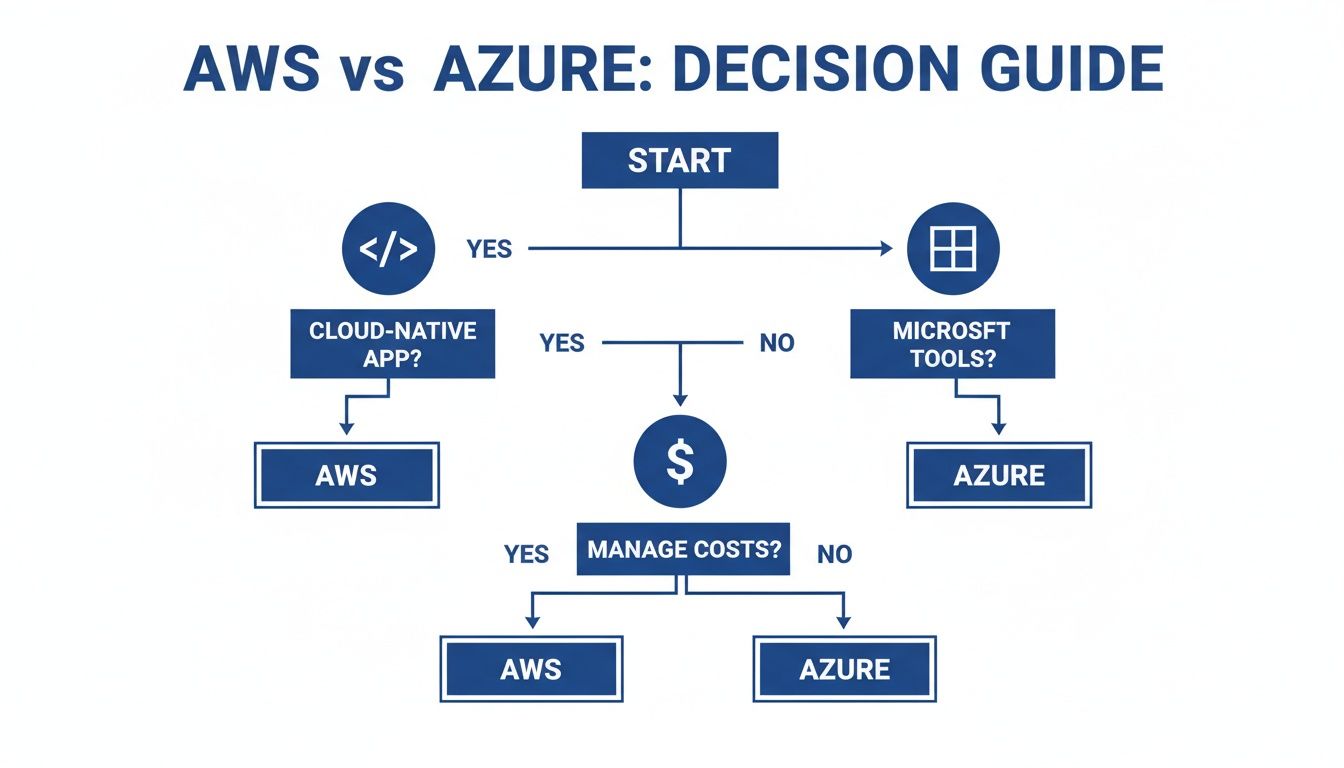
The infographic simplifies that first big fork in the road: are you focused on building new cloud-native apps, or are you extending your existing Microsoft-powered enterprise into the cloud?
The Universal Rule of Cloud Adoption
At the end of the day, when you compare AWS and Azure, there’s no single "best" answer, only the best fit for you. And the most crucial takeaway applies to everyone, no matter which path you take.
Regardless of which cloud provider you select, proactive and automated cost management is non-negotiable. From day one, implementing tools and processes to control cloud spend is the only way to ensure your cloud journey is both powerful and profitable.
Without a real strategy to manage idle resources and optimize usage, the financial perks of the cloud can disappear in a hurry. Making cost control a foundational piece of your cloud strategy is the true key to success.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Picking a cloud provider is a big decision, and it’s natural to have a few questions. The truth is, the "right" choice between AWS and Azure often boils down to your team's skills, your business goals, and the fine print. Let's clear up some of the most common questions we hear.
Think of this as bridging the gap between a glossy feature list and what it actually takes to run your business on the cloud. We'll tackle the big ones: migration, security, and which platform tends to win in certain industries.
Is It a Nightmare to Migrate from AWS to Azure (or Vice Versa)?
Let's be direct: moving between AWS and Azure is a serious project that demands careful planning. While they both offer the basics like virtual machines and databases, the way they're built, their APIs, management tools, and service setups, are fundamentally different. The real difficulty depends on how deeply you're tied into one platform's special services.
For instance, if your application leans heavily on AWS Lambda or DynamoDB, you can't just copy it over to Azure Functions or Cosmos DB. It's going to take a significant rewrite.
Some of the biggest hurdles include:
- Rewriting Your Infrastructure Code: If you're using Terraform or AWS's own CloudFormation, those templates are useless on Azure. You'll have to start over with ARM templates or Bicep.
- Database Migration: Shifting data from AWS RDS to Azure SQL is a delicate operation. You have to plan it meticulously to avoid long periods of downtime.
- Identity and Access: All those carefully crafted IAM roles and policies in AWS? They need to be manually translated into Azure Active Directory roles and permissions.
Here's the bottom line: a simple "lift and shift" is almost never that simple. The more you use a provider's unique PaaS or serverless tools, the more tangled the web becomes. It really drives home the importance of making the right choice from day one.
Which Is More Secure, AWS or Azure?
This is a classic question, but it’s a bit misleading. Both AWS and Azure pour billions into security and offer rock-solid, enterprise-level protection. Saying one is definitively "more secure" is like arguing whether a Ford is safer than a Chevy; it really depends on the driver. Security is a shared responsibility. They provide a secure foundation, but it's on you to configure everything correctly.
AWS has been around longer, and it shows in their mature security toolkit. Tools like IAM, GuardDuty, and Macie give you incredibly granular control, which is why a lot of hardcore security pros love it.
Azure, on the other hand, plays to its strengths with Microsoft's deep roots in enterprise security. Its seamless integration with Azure Active Directory is a huge win for companies already living in the Microsoft world. Plus, its security information and event management (SIEM) tool, Azure Sentinel, is incredibly well-regarded. Ultimately, both platforms give you everything you need to build a fortress; success comes down to your team’s expertise.
Is There a "Best" Choice for Certain Industries?
Absolutely. The ideal cloud provider often lines up with an industry’s unique demands, regulations, and existing tech.
- Retail and E-commerce: AWS is king here, and it makes sense given its Amazon DNA. Its massive suite of services for analytics, machine learning, and pure scalability is perfectly built for the chaos of online retail.
- Healthcare and Government: Azure has a major advantage in these highly regulated fields. Microsoft's long-standing enterprise relationships and exhaustive list of compliance certifications (like HIPAA and FedRAMP) make it a go-to for handling sensitive data.
- Financial Services: This one’s a bit of a toss-up. Many big, established banks and financial firms lean on Azure because of its strong hybrid cloud features and Microsoft integration. In contrast, the newer FinTech startups often flock to AWS for its agility and developer-centric culture.
- Startups and Tech Companies: AWS has long been the default choice for startups. It has a massive ecosystem, incredible amounts of documentation, and the kind of flexibility you need when you're trying to innovate and pivot quickly.
Choosing the right platform is the first critical step. The next is making sure you don't let your cloud bill spiral out of control from day one.
No matter which platform you choose, managing cloud costs is essential. CLOUD TOGGLE makes it easy to automate the shutdown of idle resources on both AWS and Azure, delivering predictable savings without the complexity. Start your free 30-day trial and see how much you can save at https://cloudtoggle.com.




