Choosing the right cloud provider usually comes down to a trade-off between market leadership, enterprise integration, and data innovation. AWS brings the broadest service portfolio to the table, Azure offers unbeatable integration for businesses already in the Microsoft world, and GCP leads the pack in data analytics and machine learning.
The right choice really depends on what you care about most: a mature, do-it-all ecosystem, seamless hybrid cloud capabilities, or bleeding-edge AI.
Choosing Your Cloud: A Strategic Breakdown
The whole "AWS vs Azure vs GCP" debate isn't about finding one single "best" provider. It’s more of a strategic decision that needs to align with your company's specific needs, your existing tech stack, and where you want to go in the long run.
Each of the big three cloud providers has a distinct personality and strengths, which means they naturally attract different kinds of businesses. To make a smart choice, you have to look past the marketing fluff and feature checklists and really get to the core of what each platform is about.
This comparison will cut through the noise and focus on the practical differences that actually matter. We'll frame the decision around key business goals, not just a list of technical specs.
The Big Three: An Overview
Each cloud giant has carved out its own identity in the market. Understanding these identities is the first step to finding a provider that lines up with your own strategy.
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): As the original pioneer and current market leader, AWS has the most comprehensive and battle-tested portfolio of services out there. Its massive scale and years of operational experience make it the go-to choice for startups and businesses needing a vast, reliable ecosystem for pretty much any workload.
- Azure (Microsoft): The undisputed leader in the enterprise and hybrid cloud space. Azure’s killer feature is its deep, native integration with Microsoft’s entire suite of business software, like Office 365 and Active Directory. This makes it an almost automatic choice for large organizations already heavily invested in the Microsoft stack.
- GCP (Google Cloud Platform): The specialist in data and AI. GCP is built on Google's legendary expertise in data analytics, machine learning, and container orchestration with Kubernetes. It’s the platform of choice for companies building data-heavy applications or looking to tap into the most advanced AI and ML tools available.
For a deeper look at how these providers measure up in the market, check out our detailed analysis of the latest cloud providers market share.
| Feature | AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Azure (Microsoft) | GCP (Google Cloud Platform) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Mature, comprehensive service portfolio | Enterprise and hybrid cloud integration | Data analytics, AI, and machine learning |
| Ideal For | Startups, diverse workloads, legacy apps | Large enterprises, Windows-based shops | Data-driven companies, modern apps |
| Key Differentiator | Market leadership and breadth of services | Seamless Microsoft ecosystem integration | Expertise in Kubernetes and advanced AI |
No matter which provider you go with, one challenge is universal: getting a handle on your cloud bill. A huge chunk of cloud spend comes from idle or underutilized compute resources left running after hours. This is a common pain point and highlights why a unified cost optimization strategy that works across any cloud is so important, a central theme we'll keep coming back to in this guide.
Comparing Core Compute, Storage, And Networking
When you get down to the nuts and bolts, the real differences between AWS, Azure, and GCP pop up in their core services: compute, storage, and networking. These are the absolute fundamentals of any cloud setup. For any DevOps or IT team, getting a handle on their specific quirks is essential because the choice you make here hits performance, scalability, and, most critically, your budget.
The competition in this space is intense, and it's fueling some serious market growth. In Q3 2025, the global cloud infrastructure services market ballooned to an incredible $107 billion, a 28% jump from the previous year. AWS is still the big dog with 29% market share, but Azure is closing the gap at 20%, and GCP is making impressive gains, now holding 13%. You can dig deeper into this explosive growth and see how the market is shaking out. For more detailed stats, check out the latest cloud market share data on CRN.com.
This infographic offers a great visual breakdown of the strategic thinking required when picking a provider, weighing your specific workloads against your tech stack and cost goals.
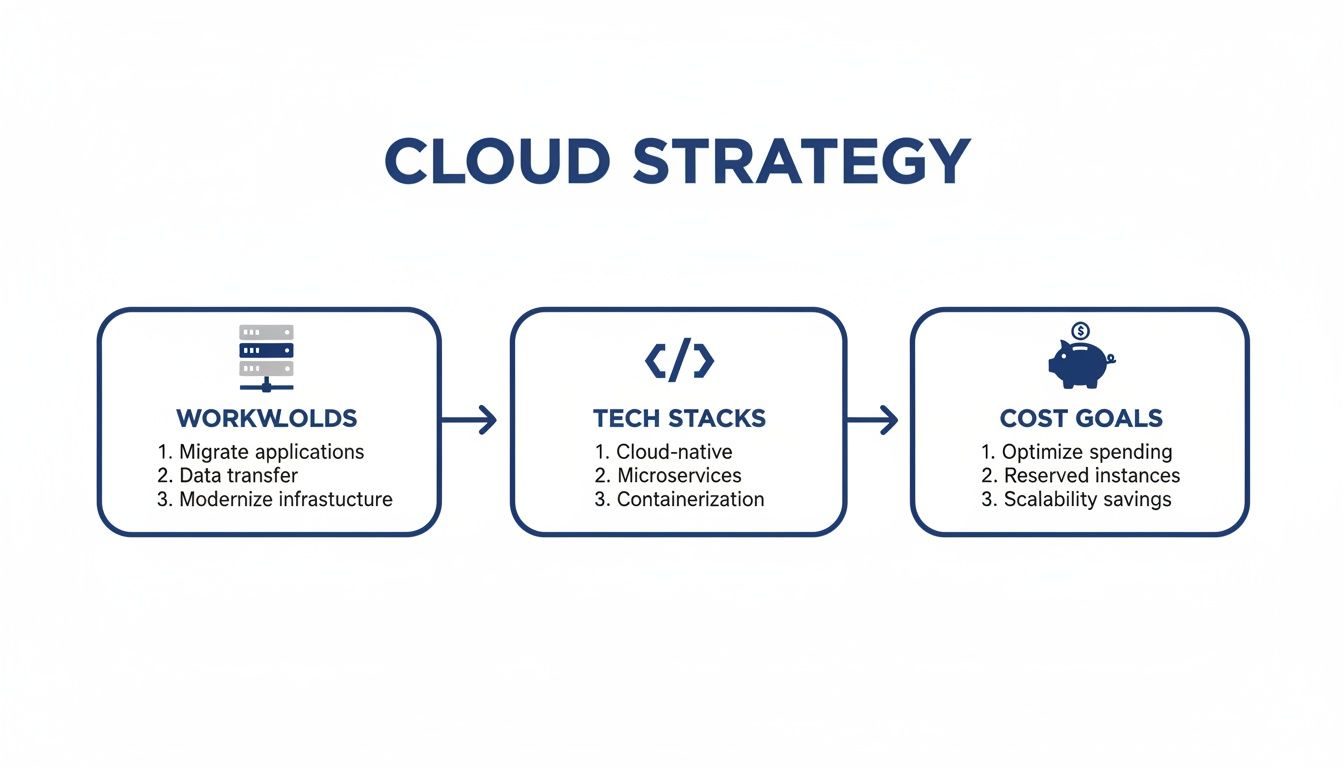
As you can see, a solid cloud strategy isn't just a tech decision; it's a business one. It's all about finding that sweet spot between what your infrastructure needs and what your budget can handle.
To make sense of the core offerings, here’s a quick side-by-side look at the flagship services from each provider. This table cuts through the noise and highlights the key differentiators you need to know for a fast evaluation.
At-a-Glance Core Service Comparison
| Service Category | AWS (Amazon Web Services) | Azure (Microsoft) | GCP (Google Cloud Platform) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute | EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Most mature, widest variety of instance types. A specialized VM for nearly every workload. | Azure Virtual Machines: Best-in-class integration with Windows Server & Microsoft ecosystem. Strong hybrid cloud features. | Google Compute Engine (GCE): Known for high performance, custom machine types, and customer-friendly pricing like per-second billing. |
| Object Storage | S3 (Simple Storage Service): The industry standard. Unmatched reliability and the largest third-party tool ecosystem. | Azure Blob Storage: High-performance and cost-effective, especially for existing Azure customers. Tiered storage (Hot, Cool, Archive). | Google Cloud Storage: Praised for speed and simplicity. Offers a single API across all storage classes and global buckets. |
| Networking | VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): The largest global footprint with the most regions and availability zones for extensive reach. | VNet (Virtual Network): Excellent hybrid networking capabilities, making on-prem to cloud connections seamless. | VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Often cited for superior performance and low latency due to its private global fiber network. |
This table gives you the 30,000-foot view, but the devil is always in the details. Let's break down what those differences mean in practice.
The Compute Engine Showdown
At the heart of any cloud platform are its virtual servers, the engines that run your applications. Each provider has a solid offering, but they’re definitely not one-size-fits-all.
-
AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): As the OG in the space, EC2 has the most exhaustive list of instance types you can find. Whether you need something optimized for general use, heavy computation, memory, or storage, AWS has a specialized machine for it. It's the dependable, do-it-all choice.
-
Azure Virtual Machines: Azure's biggest ace is its native integration with the Microsoft world. If your business runs on Windows Server, SQL Server, or other Microsoft tools, Azure VMs provide a frictionless experience and easier licensing. Their hybrid cloud capabilities are also a huge pull for established enterprises.
-
Google Compute Engine (GCE): GCE really shines on performance, especially its networking, and its pricing is often more transparent and user-friendly. Google was a pioneer in per-second billing and offers great sustained-use discounts. Plus, their custom machine types let you fine-tune resources precisely to your needs, which is a big win for avoiding waste.
Key Takeaway: Go with AWS for the most options, choose Azure if you're a Microsoft shop, and lean toward GCP for raw performance and flexible, modern pricing.
Object Storage: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Object storage is your go-to for hoarding massive amounts of unstructured data like backups, archives, and media files, you name it. All three providers offer incredibly durable and scalable solutions.
-
AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service): S3 is the undisputed industry standard. It’s known for rock-solid reliability, a deep feature set, and a sprawling ecosystem of tools that plug right into it. Its storage classes, from the instantly accessible Standard to the deep-freeze Glacier Deep Archive, give you a cost-effective home for data at any point in its lifecycle.
-
Azure Blob Storage: As a direct competitor, Blob Storage is a strong performer and is very cost-effective, particularly if you're already in the Azure ecosystem. It mirrors S3's tiering approach with Hot, Cool, and Archive options to help you manage costs based on how often you need to access your data.
-
Google Cloud Storage: GCS is all about speed and simplicity. It uses a single, high-performance API for all its storage classes, which simplifies development. A standout feature is global object access with a single bucket name, making data management for distributed applications much cleaner.
Networking And Global Reach
Your provider’s network is what connects your applications to your users securely and quickly. Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) are the foundation here, letting you carve out your own isolated slice of the cloud.
The core products are functionally very similar:
- AWS VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- Azure VNet (Virtual Network)
- Google VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
All three deliver the robust security features you’d expect, like subnets, firewalls, and routing tables. The real differentiators are in their global network performance and underlying architecture.
Google's premium network tier is often lauded for its top-tier performance and low latency because it routes traffic over its own private global fiber network. On the other hand, AWS has the largest number of regions and availability zones, giving it unparalleled global coverage. Azure finds a middle ground, offering a massive global footprint along with standout hybrid networking features that make linking on-prem data centers to the cloud a breeze.
Evaluating Managed Services And AI Capabilities
While core compute and storage get all the attention, the real magic happens in the advanced managed services and AI capabilities. This is where the big three cloud providers truly show their cards, moving beyond basic infrastructure to offer tools that let you offload operations and actually innovate.
For any CTO, the decision here is less about features and more about vision. It's about picking the ecosystem that will best accelerate your specific data and innovation goals. You're not just buying services; you're aligning with a strategic partner.
AWS: The Mature And Broad Ecosystem
As the first mover, AWS simply has the deepest and most mature collection of managed services. If you can think of a problem, they probably have a battle-tested service for it.
Take Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service). It completely automates the tedious parts of running a database like provisioning, patching, and backups, so your team can focus on the application itself. It just works.
Then there's AWS Lambda, the service that made "serverless" a household name. It lets you run code without ever thinking about a server, scaling effortlessly from a handful of requests to thousands per second. The sheer size of the AWS ecosystem means there's a managed solution for nearly anything, making it a safe, reliable bet. You can find out more about the different cloud services and solutions available to get your projects moving faster.
Azure: Enterprise Integration And OpenAI Leadership
Microsoft Azure's home-field advantage is its flawless integration with the entire Microsoft enterprise stack. For companies already running on tools like Microsoft 365 and Active Directory, choosing Azure is a no-brainer.
But where Azure is really turning heads now is its exclusive partnership with OpenAI. Through Azure AI services, including the Azure OpenAI Service, businesses get direct, secure access to powerful models like GPT-4. This has cemented Azure's position as the go-to platform for enterprises looking to build generative AI solutions with the security and compliance they already trust.
This tight coupling with OpenAI gives Azure a massive edge. It lets companies build on the world's most advanced AI models inside a familiar, enterprise-grade cloud environment. That’s a huge draw for any business serious about generative AI.
GCP: Data Analytics And AI Specialization
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) may be smaller by market share, but it punches way above its weight in data analytics and AI. This isn't surprising, given Google’s own history of managing planetary-scale data and pioneering machine learning. It’s why GCP handles 20% of healthcare and finance workloads, even with a market share around 13%.
Services like BigQuery and Vertex AI are the crown jewels here. BigQuery is a serverless data warehouse that lets you run SQL queries over enormous datasets in seconds. It has become an industry standard for a reason.
Vertex AI is a unified platform that simplifies the entire machine learning workflow, from building and training models to deploying them at scale. If your business lives and breathes data, GCP’s specialized tools offer a compelling advantage. Add in its leadership with Kubernetes (which started at Google), and you have the undisputed champion for modern, containerized applications.
Understanding Cloud Pricing And Cost Management
Trying to decipher the pricing models for AWS, Azure, and GCP can feel like reading a map in a foreign language. Each provider lays out a complex web of options tailored to different use cases, making a straight "apples-to-apples" comparison almost impossible. For any FinOps team or business owner, getting a handle on these nuances is the first critical step to preventing a cloud bill from spiraling out of control.
On the surface, all three giants build their pricing on a pay-as-you-go foundation. But the devil is in the details. Small differences, like per-second versus per-minute billing, can have a surprisingly big impact. GCP was an early leader in customer-friendly billing by offering per-second billing for most of its VMs, a practice AWS and Azure have since adopted for many of their own services.
That tiny detail matters for short-lived workloads, like the kind you find spinning up and down in dev or test environments. The real, substantial savings, however, come when you move past on-demand rates and commit to longer-term usage.

Commitment And Discount Models
To reward loyalty and predictable workloads, each provider rolls out the red carpet with deep discounts for upfront commitments. The names are different, but the idea is the same: promise you'll use a certain amount of compute for one or three years, and they'll give you a steep price cut.
-
AWS Reserved Instances & Savings Plans: AWS gives you two main paths. Reserved Instances (RIs) offer the biggest discounts of up to 72%, but they lock you into a specific instance family in a specific region. Savings Plans are much more flexible, offering a nice discount in exchange for committing to a certain hourly spend.
-
Azure Reserved Savings & Hybrid Benefit: Azure’s Reserved Virtual Machine Instances work a lot like AWS RIs. But Azure has a trump card: the Azure Hybrid Benefit. This lets businesses bring their existing on-premise Windows Server and SQL Server licenses to the cloud, which can translate into massive savings.
-
GCP Committed Use Discounts (CUDs): GCP’s CUDs are generally seen as more flexible than AWS RIs. They're tied to a project and apply to the total vCPUs and memory you use, not specific instance types. This makes them much easier to manage as your needs change.
For workloads that can handle interruptions, there's another pricing tier that delivers even more dramatic savings. Spot Instances (AWS), Spot Virtual Machines (Azure), and Spot VMs (GCP) let you buy up unused compute capacity at discounts reaching up to 90%. The catch? The provider can yank that capacity back with little notice, making them perfect for fault-tolerant jobs like batch processing but a total non-starter for critical applications.
Native Cost Management Tools
As cloud bills became more complex, each provider launched its own suite of tools to help customers track, manage, and forecast their spending. These native tools are powerful, but they often come with a steep learning curve and some serious limitations.
A head-to-head comparison of pricing between AWS vs Azure shows just how granular you have to get to find the best deal for your specific workload.
The biggest problem with native cost tools is that they are siloed. They work great within their own ecosystem but give you zero visibility into a multi-cloud setup. This forces your team to learn and juggle multiple complex platforms, leading to operational headaches and fragmented reports.
Here’s a quick rundown of what each provider offers:
| Provider | Primary Tool | Key Features | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | AWS Cost Explorer | Detailed cost reports, forecasting, and recommendations for Reserved Instances and Savings Plans. | Can be overwhelming for non-technical users and offers no multi-cloud visibility. |
| Azure | Azure Cost Management | Budgeting, alerts, cost analysis, and optimization tips. It's tightly integrated into the Azure portal. | Focused almost entirely on Azure services, with limited options for creating granular, targeted alerts. |
| GCP | Cloud Billing Tools | Cost dashboards, budget alerts, and detailed reports. Anomaly detection is a nice default feature. | Offers less customization for alerts and reporting when compared to AWS or third-party tools. |
While these tools are a necessary first step, they often fall short in one critical area: proactively stopping idle compute costs. They’re great at showing you where you spent money last month, but they are far less effective at automatically stopping the waste from happening in the first place. This is precisely the gap where specialized third-party platforms step in, simplifying the process of shutting down non-production resources to deliver immediate, predictable savings without all the complexity.
How To Choose The Right Cloud Provider
Picking the right cloud provider in the AWS vs Azure vs GCP debate isn't about finding a single "best" platform. It's about matching a provider’s core strengths to your specific business reality. The decision really comes down to your existing tech stack, your team's skills, and your long-term goals. A choice that helps one company fly could easily create drag for another.
Making the right call means looking past the feature checklists and focusing on what fits your situation. A startup with zero legacy hardware has completely different needs than a global enterprise juggling a complex hybrid setup.

When To Choose AWS
There's a reason AWS is the default choice for so many. Its mature, sprawling ecosystem offers a tool for pretty much any problem you can imagine, making it a solid platform for a huge range of businesses.
You should seriously consider AWS if:
- You're a startup that needs to move fast. The massive menu of services and a generous free tier let new companies experiment and scale quickly without a huge upfront investment. Plus, the extensive documentation and community support really lower the barrier to entry.
- Your organization needs the absolute broadest range of services. From niche databases to IoT and even satellite ground stations, the AWS portfolio is just unmatched. If you want a one-stop shop, AWS is it.
- You have diverse and unpredictable workloads. The sheer variety of EC2 instance types and flexible pricing models like Savings Plans give you the tools to optimize costs for almost any application.
AWS stays the market leader because it’s a jack of all trades and a master of quite a few. Its reliability and scale make it a safe, powerful bet for organizations that value a proven track record and the widest possible set of tools.
When To Choose Azure
Microsoft Azure has played its hand masterfully, creating an unbeatable value proposition for a huge chunk of the market. Its growth has been nothing short of remarkable.
Microsoft Azure has successfully grabbed 23-24% of the global market share, with a staggering 85% of Fortune 500 companies now using its platform. This impressive adoption is fueled by its native integration with essential enterprise tools like Microsoft 365 and Active Directory, making it a no-brainer for businesses already in the Microsoft world. You can find more details on Azure's market performance on turbo360.com.
Azure is the logical choice when:
- Your company is heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. The integration with Windows Server, SQL Server, Office 365, and Active Directory is completely seamless. This simplifies management and often cuts costs through programs like the Azure Hybrid Benefit.
- You're building out a hybrid cloud environment. Azure was practically built for hybrid. Tools like Azure Arc and Azure Stack make it far easier to manage resources that live across your on-prem data centers and the public cloud.
- Your focus is on enterprise-grade AI with strong governance. Azure’s exclusive partnership with OpenAI gives you secure, compliant access to advanced models like GPT-4 inside a trusted corporate environment.
When To Choose GCP
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is the specialist. It excels in the areas where its parent company’s DNA shines brightest: data, networking, and modern app development.
GCP is your best bet if:
- Your business lives and breathes big data and machine learning. Services like BigQuery for data warehousing and Vertex AI for ML workflows are widely considered best-in-class. GCP is simply built to chew through massive datasets with incredible speed.
- You're building cloud-native, containerized applications. As the birthplace of Kubernetes, GCP offers the most advanced and integrated managed Kubernetes service (GKE). This makes it the top pick for DevOps teams committed to a container-first strategy.
- Performance and a high-speed global network are non-negotiable. Google’s private global fiber network often delivers lower latency, which can be a game-changer for applications that need to move data across continents quickly.
At the end of the day, the decision might not be to pick just one. A multi-cloud strategy, where you use services from two or even all three providers, is becoming more and more common. This approach lets you cherry-pick the best tool for each job, avoid vendor lock-in, and build a more resilient infrastructure overall.
Still Have Questions About Cloud Providers?
You're not alone. When you get down to the brass tacks of AWS vs. Azure vs. GCP, a few key questions always pop up. Let's tackle them head-on.
Which Cloud Provider Is The Cheapest For A Small Business?
Honestly, there's no single "cheapest" provider; it all boils down to your specific workload. If you’re running certain kinds of compute instances, GCP might give you the best price. If you’re a startup just testing the waters, the generous AWS free tier is hard to beat. But for businesses already running on Microsoft software, Azure often comes out on top thanks to major licensing discounts.
The only way to know for sure is to model your expected usage. Don't get distracted by the sticker price on a website; compare costs based on the actual services you'll be running day in and day out.
Can I Use Services From All Three Clouds At The Same Time?
Absolutely. This is called a multi-cloud strategy, and it's becoming more common. Many teams do this to cherry-pick the best services from each provider, avoid getting locked into one ecosystem, and build more resilient applications.
For instance, you might use GCP for its top-tier data analytics, AWS for its sheer breadth of services, and Azure for its seamless integration with your existing enterprise tools. Just be aware that managing a multi-cloud setup introduces new headaches for cost management, security, and daily operations.
The real power of a multi-cloud strategy is picking the best tool for the job, every time. This flexibility can be a massive competitive advantage, but it demands careful planning to handle the extra operational weight.
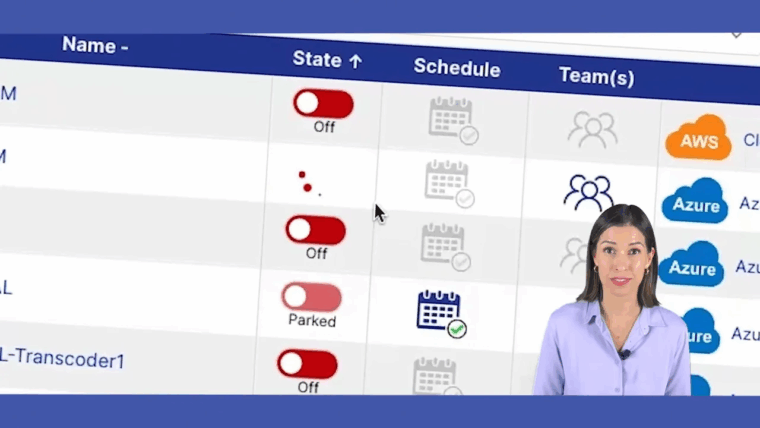
How Much Can I Save By Turning Off Idle Servers?
The savings from shutting down idle servers are huge; we're not talking about pocket change. On average, companies slash their cloud compute bills by 20-40%, sometimes even more. The best part? It's often as simple as setting up an automated schedule to power down non-production resources after business hours.
Your development, testing, and staging environments are the biggest culprits here. This one simple habit of stopping resource waste delivers an immediate and significant return on investment.
Ready to stop wasting money on idle cloud resources? CLOUD TOGGLE makes it easy to automate server shutdowns and cut your AWS and Azure bills. Start your 30-day free trial and see how much you can save.