When you get down to it, the AWS vs GCP vs Azure debate really comes down to their market position and core strategy. AWS is the established leader with a massive service catalog, Azure owns the enterprise space thanks to its deep integration with Microsoft products, and GCP is the specialist in data analytics and machine learning.
Your choice boils down to what you value most: the broadest possible toolkit, seamless integration with your existing enterprise software, or best-in-class data tools.
The Three Giants of Cloud Computing
Choosing a cloud provider is a massive decision, one that sets the foundation for everything from your app's performance to your monthly budget. The market is run by three titans, and each one has a unique history and philosophy that shapes what they offer. Understanding these personalities is the first step to picking a partner that truly fits your business goals.
This is especially true for small and midsize businesses (SMBs). With limited resources, the right platform can give you a serious leg up on the competition. The wrong one? You could be looking at vendor lock-in, surprise bills, and a lot of operational headaches.
Market Position and Strengths
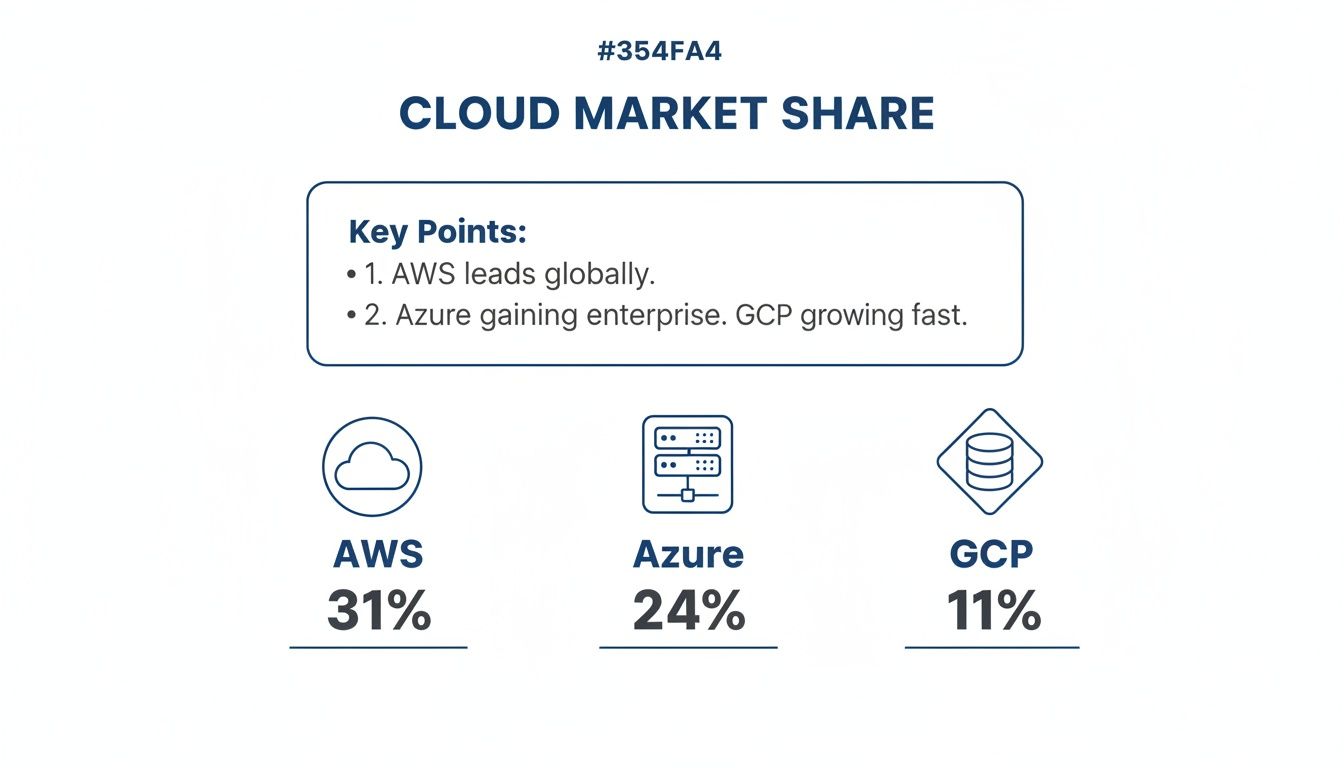
The cloud market is anything but static. While AWS still wears the crown as the market leader with a hefty 29-32% global market share, both Azure and GCP are gaining ground at an impressive clip.
Recent data shows AWS holding around 29% of the cloud infrastructure market, with Microsoft Azure sitting comfortably at 20%. Google Cloud is a strong contender at 12-13%. Combined, these three control over 62% of the entire market, which makes taking a closer look at the cloud providers market share a critical step in your strategic planning.
This market breakdown isn't just about numbers; it translates directly into the core strengths of each provider.
AWS vs GCP vs Azure At a Glance
To quickly frame the comparison, here’s a high-level look at where each provider stands. This table gives you a snapshot of their market position, what they do best, and who they’re typically for.
| Provider | Market Share | Core Strength | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | 29-32% | Mature ecosystem, widest service portfolio, reliability | Businesses needing a broad, flexible set of tools and maximum scalability. |
| Azure | 20-24% | Enterprise integration, hybrid cloud, strong PaaS offerings | Organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft software ecosystem. |
| GCP | 11-13% | Big data, analytics, machine learning, containerization | Data-centric startups and companies focused on modern, cloud-native development. |
This gives us a starting point, but the real story is in the details of their services, pricing, and overall philosophy.
No matter which platform you lean toward, one challenge is universal: keeping costs under control. One of the biggest money pits for any business is paying for idle resources, servers that run 24/7 even when they’re only needed during business hours. This quiet, consistent waste is a primary reason cloud bills get out of hand, making cost management a vital skill from day one.
Comparing Core Cloud Services
To get to the heart of the AWS vs GCP vs Azure debate, you have to look at their core services. On the surface, they all offer the essentials, compute, storage, and networking, but the way they deliver them, their performance quirks, and feature depth are worlds apart. Nailing down these differences is how you pick a platform that actually fits what your business and tech teams need.
This chart paints a clear picture of where things stand in the cloud market today.
There’s no mistaking AWS's long-standing dominance. But Azure is a powerful number two, and GCP is a serious contender, each with its own loyal following.
Compute Power and Virtual Machines
Compute is the engine room of any cloud platform. It’s where your code runs, and each provider puts its own spin on virtual machines (VMs).
-
AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is all about choice. With hundreds of instance types built for everything from general computing to memory-heavy tasks and specialized AI workloads, the flexibility is massive. But that massive catalog can be a double-edged sword; it’s powerful for seasoned teams but can easily cause decision fatigue for newcomers.
-
Azure Virtual Machines is Microsoft’s EC2 equivalent, and its killer feature is its tight integration with the Windows world. If you have existing Windows Server licenses, the Azure Hybrid Benefit can unlock serious savings. Azure keeps its instance families more structured, which makes it a bit less intimidating to navigate than AWS’s sprawling options.
-
GCP Compute Engine has a reputation for raw performance and some genuinely user-friendly perks. Google frequently tops the charts in network throughput and offers live VM migration, a fantastic feature that cuts down on downtime when host systems need maintenance. Plus, its custom machine types let you dial in the exact vCPU and memory you need, which is a great way to avoid paying for resources you don't use.
Key Takeaway: Go with AWS if you need the absolute widest selection of instances. Choose Azure if your business runs on Microsoft. Pick GCP for top-tier performance and fine-grained cost control.
Cloud Storage Solutions
You can't build anything in the cloud without reliable, scalable storage. All three giants deliver solid object storage services built for insane durability and easy access.
AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) is pretty much the industry blueprint for object storage. It promises 99.999999999% (that’s eleven 9s) of durability and gives you a ton of storage classes, from S3 Standard for hot data to S3 Glacier Deep Archive for dirt-cheap long-term cold storage. Its age is an advantage, nearly every third-party tool out there integrates with S3.
Azure Blob Storage goes head-to-head with S3, offering similar durability and tiered options (hot, cool, and archive). Its main strength is how well it plays with other Azure services, making it the default choice for anyone building on the Azure stack.
Google Cloud Storage keeps things simpler with fewer storage tiers, which can be a relief for new users. Its standout feature is the ability to have objects from different storage classes inside a single bucket. That kind of flexibility, combined with its zippy access speeds, makes it a beast for data analytics and media delivery.
Networking and Content Delivery
A fast, reliable network is what connects your cloud resources to the world. All three providers have sophisticated virtual private clouds (VPCs) and load balancers.
But when you need to serve users globally, their Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are what matter most.
- AWS CloudFront is the most mature player, with a massive global web of edge locations that helps keep latency low for users no matter where they are.
- Azure CDN is interesting because it lets you use third-party CDN providers in addition to its own network, giving you more options.
- Google Cloud CDN runs on the same premium global network that powers Google Search and YouTube. That pedigree often translates to truly exceptional performance.
Managed Database Services
Databases are the foundation of most modern applications, and managed services take the pain out of deploying, patching, and scaling them.
AWS and Azure both have a massive menu of database choices. AWS offers Amazon RDS for classic relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL, plus specialized tools like DynamoDB for NoSQL. Azure answers with Azure SQL Database and its globally distributed, multi-model database, Azure Cosmos DB.
When you’re comparing the core cloud services and solutions, it's worth digging into the nuances of their nonrelational database offerings. GCP’s Cloud SQL is a solid relational option, but its crown jewel is Cloud Spanner. It’s a globally distributed relational database that gives you the transactional consistency of old-school databases with the horizontal scale of NoSQL. For applications that need to be strongly consistent across the globe, that’s a game-changer.
AI and Machine Learning Platforms
This is where the real fight is. AI and ML are the front lines of the AWS vs GCP vs Azure rivalry, and each platform has a distinct personality.
Google Cloud Platform is often seen as the leader here. It’s built on decades of internal research from Google Brain and DeepMind, and it shows. Services like Vertex AI make building and deploying ML models incredibly powerful yet approachable, and its pre-trained APIs for vision, speech, and translation are widely considered the best in the business.
AWS brings the most comprehensive toolkit with Amazon SageMaker, a fully managed platform that covers the entire ML lifecycle. It offers incredible depth and control, making it the go-to for data scientists who want to tweak every part of the model-building process.
Azure Machine Learning Studio shines with its user-friendly, drag-and-drop interface. It opens up machine learning to developers who aren't data science PhDs. Its strong focus on responsible AI and enterprise-level security also makes it a very attractive option for larger, compliance-focused companies.
Decoding Cloud Pricing and Discount Models
Trying to make sense of cloud pricing can feel like a puzzle where the pieces keep changing. The AWS vs GCP vs Azure debate gets particularly tricky here because each provider has a completely different billing philosophy, which can seriously swing your monthly bill. To get a real grip on your costs, you have to look past the sticker price and dig into their discount models.

Sure, they all offer a pay-as-you-go option, but the real savings come when you commit. The challenge is figuring out which discount structure actually fits how your company uses resources.
On-Demand and Pay-As-You-Go Rates
This is the default, no-strings-attached pricing tier. You pay a set rate for what you use, usually billed by the second or minute, with zero long-term commitment. It's the perfect fit for unpredictable workloads, quick projects, or when you're just starting out and have no idea what you'll need.
But let's be clear: relying only on on-demand pricing is almost always the most expensive way to run your infrastructure in the long run. GCP used to have an edge with per-second billing on more services, but AWS and Azure have pretty much closed that gap, making it less of a deciding factor.
Reserved Instances and Commitment-Based Discounts
This is where a little planning goes a long way. All three giants will reward you for committing to a certain amount of resource usage over a one or three-year term.
- AWS Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans: AWS gives you two main ways to save. RIs have you commit to a specific instance family in a particular region. Savings Plans are way more flexible, you just commit to a certain dollar amount per hour, and it applies across different instance types and even regions.
- Azure Reserved Virtual Machine Instances: This works a lot like AWS RIs, with discounts for one or three-year terms. The standout feature here is the Azure Hybrid Benefit, which lets you use your existing on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses in the cloud for massive savings. It’s a game-changer for Microsoft shops.
- GCP Committed Use Discounts (CUDs): GCP’s model is widely seen as the most straightforward. Instead of locking into specific instances, you commit to a certain amount of vCPU and memory usage in a region. The discounts are then applied automatically wherever they fit. Simple.
Key Differentiator: GCP also has something called Sustained Use Discounts, which automatically kick in with small savings when instances run for a big chunk of the month. You get rewarded for consistent usage without having to do a thing.
Spot Instances for Maximum Savings
Got workloads that can be interrupted? Spot Instances offer the biggest discounts you can find, often slashing on-demand prices by up to 90%. You're basically bidding on spare compute capacity that the cloud provider isn't using.
This is a fantastic model for things like batch processing, data analysis, or dev/test environments that don't need to be up 24/7. The catch is that the provider can pull the plug with very little warning, so your application has to be built to handle that. Azure calls them Spot VMs, and GCP has Preemptible VMs, but the concept is the same.
Getting these pricing layers right is fundamental to managing your overall cost of cloud infrastructure.
Cloud Pricing and Discount Models Compared
To help cut through the noise, this table breaks down the main discount options and what makes them different across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
| Pricing Model | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commitment Discount | Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans (1 or 3-year term). | Azure Reservations (1 or 3-year term). | Committed Use Discounts (CUDs) (1 or 3-year term). |
| Flexibility | Savings Plans offer good flexibility; RIs are more rigid. | Standard reservations are specific; some flexibility is available. | CUDs are highly flexible, applying to resource pools. |
| Unique Feature | Broadest range of options with Convertible RIs and multiple Savings Plans. | Azure Hybrid Benefit allows using on-premises licenses for big savings. | Sustained Use Discounts apply automatically without any commitment. |
| Deepest Discount Model | Spot Instances (up to 90% off). | Spot Virtual Machines (up to 90% off). | Preemptible VMs (up to 80% off). |
So, who wins the AWS vs GCP vs Azure pricing showdown? It really depends on how predictable your workloads are and how much time your team wants to spend managing commitments. If your needs are all over the place, GCP’s automatic discounts make saving money easy. If you're a big Microsoft enterprise, Azure's Hybrid Benefit is almost impossible to beat. AWS offers the most detailed control, which is powerful if you have the resources to manage it actively.
Finding the Right Cloud for Your Business
Once you get past the spec sheets for compute instances and storage tiers, the real decision in the AWS vs GCP vs Azure debate comes down to your company's unique DNA. The best cloud provider isn't the one with the longest feature list. It's the one that clicks with your existing tech stack, your team's skills, and your long-term goals. This is where we move from theory to what actually works in the real world.
Each of these platforms was built with a core audience in mind. Figuring out which profile your business fits is the clearest path to a smart decision. The choice you make will ripple through everything, from developer productivity to how fast you can innovate.
The Microsoft-Centric Enterprise
For businesses already living in the Microsoft universe, Azure is almost always the path of least resistance. If your daily operations run on Windows Server, Office 365, SQL Server, and Active Directory, Azure feels less like a new platform and more like a natural extension of your current IT infrastructure.
This deep integration isn't just a nice-to-have; it delivers real, tangible benefits. The Azure Hybrid Benefit, for instance, lets you use your on-premises Windows Server and SQL Server licenses in Azure, which can slash your cloud bill. Your IT staff and developers, already fluent in Microsoft tools, can get moving much faster, cutting down training time and speeding up your move to the cloud.
For a Microsoft-heavy business, adopting Azure is less a migration and more an evolution. You're building on a foundation your team already knows and trusts, which makes the jump to a hybrid or full-cloud setup far smoother and more cost-effective.
When your entire productivity suite and identity management are already tied to Microsoft, adding Azure creates a single, powerful ecosystem. It's a huge reason so many established companies lean this way.
The Azure portal, shown below, is designed to give you a single pane of glass for managing this sprawling ecosystem.
This centralized dashboard is a big part of Azure's appeal, offering a familiar interface for teams juggling both on-prem Microsoft products and new cloud services.
The Data-Driven Startup
If your startup’s secret sauce is data, machine learning, or AI, you need to give Google Cloud Platform (GCP) a hard look. GCP’s identity is forged from Google's own internal infrastructure, the same beast that powers Search, YouTube, and Maps. That heritage gives it a serious edge in big data analytics and AI.
Services like BigQuery for serverless data warehousing and Vertex AI for managing the entire machine learning workflow are consistently praised as best-in-class. For startups aiming to chew through massive datasets or build complex predictive models, GCP's toolset offers a massive head start. Its dedication to open-source tech, especially Kubernetes (which started at Google), also makes it a perfect fit for modern, cloud-native development.
On top of that, GCP’s simpler, more transparent pricing can be a lifesaver for startups trying to keep their budget predictable. The platform's culture of innovation and its laser focus on advanced data services make it an ideal partner for businesses built to win with data.
The Market Leader and Innovator
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is still the default choice for a huge number of businesses, from scrappy startups to global corporations. The reason is simple: unmatched maturity and the sheer breadth of its services. As the OG of the cloud space, AWS has had years to build out the most comprehensive portfolio of tools and solutions on the market.
This massive ecosystem means that no matter what problem you're trying to solve or what new direction you pivot to, there’s almost certainly an AWS service ready to handle it. This makes AWS an incredibly safe and flexible choice for companies that need a platform that can support any idea they dream up. The vast documentation, a huge user community, and extensive third-party tool support create a powerful safety net.
However, Azure’s incredible growth has made it a true powerhouse, now holding 23-24% of the market and winning over 85% of Fortune 500 companies. Its expansion, driven by a $13 billion AI business and its seamless Microsoft integration, makes it a go-to choice for SMBs in finance and manufacturing looking for solid hybrid cloud solutions.
When making a decision this big, businesses, especially SMBs, have to think about compliance. For example, knowing how SOC 2 certification can unlock deals for startups and SMBs is vital. This requirement can directly influence which provider’s security and governance tools are the right fit. Choosing a platform that makes compliance easier from day one can be a major competitive advantage.
Optimizing Cloud Costs Beyond Native Tools
Picking the right platform in the AWS vs GCP vs Azure showdown is only half the battle. Regardless of which provider you choose, a universal challenge is waiting: the silent but relentless drain of cloud waste. Even with the perfect services, your monthly bill can spiral if you aren't actively managing how and when your resources run.
This problem is most obvious with idle compute resources. Many companies leave non-production servers, like those for development, staging, and QA, running 24/7. In reality, these environments are often only needed for about 40-50 hours per week. This means a shocking amount of money, often 20-40% of a company's total cloud spend, is wasted on evenings and weekends when no one is working.

This isn't an issue unique to one provider. For DevOps teams in multi-cloud setups, GCP Compute Engine idle waste often mirrors the 25-35% seen in AWS and Azure. While Google Cloud has fought its way back to an 11-13% market share, largely on the back of its AI dominance, the core challenge of idle resources is the same everywhere. You can dig deeper into GCP's market position and what it means for SMBs at marketwise.com.
The Limits of Native Scheduling Tools
Recognizing this issue, the big cloud providers offer their own native tools to help automate resource shutdowns. But let's be honest, these solutions often fall short for teams that need a simple, scalable, and user-friendly way to manage costs.
- AWS Instance Scheduler requires you to deploy a complex CloudFormation template, configure DynamoDB tables, and wrangle IAM roles. It’s powerful, sure, but it's a cumbersome tool that demands serious technical expertise to get running and keep running.
- Azure Automation Start/Stop VMs v2 is just as complicated, leaning on Logic Apps and Azure Functions. It works, but it creates a maintenance headache and isn't exactly intuitive for non-engineers who might need to manage schedules.
Both native options lack a simple, central UI and make it tough to delegate scheduling without handing over broad account permissions. They're engineered solutions, not user-friendly products.
The core problem with native tools is they treat cost optimization as an engineering problem, not a business one. They’re built for developers who can write scripts and manage infrastructure, effectively shutting out finance teams, project managers, and others who have a direct stake in controlling costs.
This complexity creates a real barrier to effective cost management. It leaves significant savings on the table simply because the tools are too hard to use.
A Purpose-Built Solution for Cost Control
This is exactly where third-party platforms designed for cloud cost optimization show their value. A solution like CLOUD TOGGLE directly tackles the shortcomings of native tools by focusing on simplicity, accessibility, and multi-cloud management. It gives you a straightforward way to stop idle resource waste without all the technical overhead.
The platform has several clear advantages over the native schedulers:
- Intuitive UI: An easy-to-use interface lets anyone, technical or not, set up and manage schedules in minutes.
- Role-Based Access: You can safely delegate scheduling controls to non-engineers without giving them the keys to your entire cloud account. This empowers teams to manage their own resource costs responsibly.
- Centralized Dashboard: For businesses running in a multi-cloud environment, it provides a single pane of glass to manage schedules across AWS, Azure, and GCP, unifying your cost-saving efforts.
By automating the shutdown of non-production instances during off-hours, you can immediately reclaim a huge chunk of your cloud budget. It's a simple strategy that delivers predictable savings and encourages your entire organization to build a culture of cost awareness, turning a persistent challenge into a sustainable win.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're trying to figure out the AWS vs GCP vs Azure landscape, a few common questions always pop up. Let's tackle them head-on, because getting these foundational pieces right helps you build a cloud environment that actually works for your business, without the sticker shock.
Which Cloud Is Best For a Small Business?
There’s no single "best" cloud for a small business. The right choice really comes down to your team's background and what you’re trying to build.
If your team lives and breathes Microsoft products like Windows Server and Office 365, then Azure is almost always the path of least resistance. The integration is baked in, the learning curve is gentler, and you might even get some pricing perks. On the other hand, if you're building something that leans heavily on data analytics or machine learning, GCP’s strengths in those areas and its simpler pricing can be a game-changer.
And what about AWS? It’s the seasoned all-rounder. Its service catalog is so massive that no matter how your business grows or what new problem you need to solve, AWS likely has a tool for it. My advice? Look at your main workload first and pick the provider that makes that one thing easiest.
Is It a Good Idea To Use Multiple Cloud Providers?
Going multi-cloud, using services from more than one provider, sounds great in theory. You avoid getting locked into one vendor and can cherry-pick the absolute best tool for every job. It’s a powerful strategy, but it comes with a big catch.
The reality is that managing multiple clouds adds a ton of complexity to everything from security to billing. For most small and midsize businesses, it’s far more practical to start with a single provider. This keeps your operations simple and your security tight. Once you’re more mature, you can strategically bring in a second provider for a specific, high-value reason.
A multi-cloud approach magnifies the need for centralized management tools. Without a unified view, costs and operational tasks can quickly become chaotic, undermining the benefits you sought to gain.
This is exactly where tools that give you a single pane of glass become non-negotiable for keeping things under control.
What Is the Biggest Hidden Cost in the Cloud?
Without a doubt, the single biggest hidden cost in the cloud is idle resources. It happens all the time. Teams spin up servers for development, testing, or staging, but those machines are only really used during business hours.
The problem is, they’re often left running 24/7. That means you’re paying for them all night, over the weekend, and on holidays while they deliver zero value. This waste can easily eat up 20-40% of a company’s entire compute budget. Sure, things like data transfer fees can be surprising, but nothing comes close to the sheer financial drain of idle compute.
Automating the shutdown of these non-production resources is the quickest way to see immediate, predictable savings. It’s a foundational step for any business that’s serious about managing its cloud spend.
Stop wasting money on idle cloud resources. With CLOUD TOGGLE, you can easily automate server shutdowns and cut your AWS and Azure bills by up to 40%. Get started with a 30-day free trial and see your savings in action. Learn more at https://cloudtoggle.com.




