In any competitive market, controlling expenses is not just a financial exercise; it's a strategic imperative. For IT and cloud teams, mounting infrastructure costs can quickly erode budgets and hinder innovation. The challenge lies in finding effective strategies to reduce costs that deliver substantial savings without compromising performance, reliability, or security. This is where tactical, well-planned optimization becomes a critical business function rather than a mere background task.
This article moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roundup of 10 proven strategies tailored for operational efficiency. We will deliver actionable steps, real-world examples, and specific tools you can implement immediately to see a tangible impact on your bottom line. You will learn precisely how to transform potential cost centers into models of efficiency and value.
The goal is to equip you with a prioritized, actionable playbook. From leveraging lean manufacturing principles in your digital workflows to optimizing your entire operational footprint through automation and supply chain enhancements, these insights are designed for direct application. We will explore the methods that leading organizations use to cut expenses systematically and reinvest those savings directly into growth initiatives. Let's dive into the practical techniques that will help you achieve significant and sustainable cost reduction.
1. Master Idle Resource Scheduling
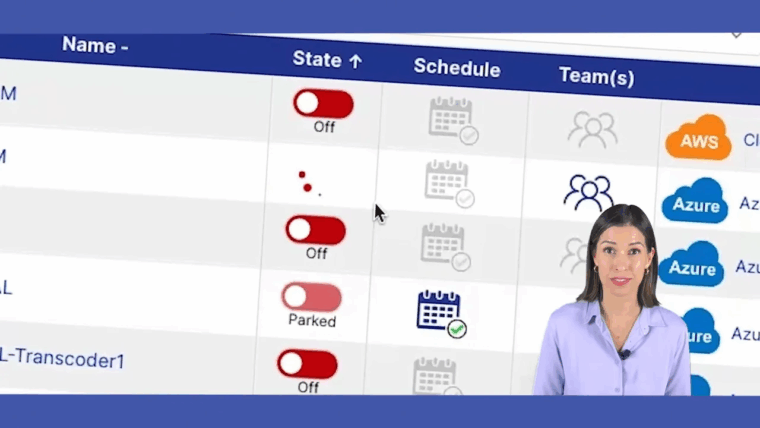
One of the most significant and often overlooked sources of wasted cloud expenditure is idle compute resources. Virtual machines and servers for development, testing, and staging environments frequently run 24/7, even though they are only actively used during standard business hours. Implementing an automated scheduling system to power down these non-production resources during off-hours, like nights and weekends, is one of the most effective strategies to reduce costs.
This "start/stop" or "on/off" scheduling approach provides immediate and predictable savings with minimal operational disruption. By simply turning off an instance when it's not needed, you stop paying for its compute time, which can lead to massive cost reductions.
Key Insight: For a typical Monday-to-Friday, 9-to-5 work schedule, non-production resources are only needed for about 45 hours a week. By shutting them down for the remaining 123 hours, you can cut compute costs for those specific instances by over 70%.
How to Implement Resource Scheduling
Getting started with idle resource scheduling is a straightforward process that delivers a high return on investment.
- Tag Your Resources: The first step is to identify and tag all non-production resources. Use a consistent tagging schema, such as
environment:devorusage:qa, to clearly distinguish which assets can be safely powered down. - Establish a Clear Policy: Communicate the new scheduling policy to all relevant teams. Define the standard "on" hours and establish a simple process for requesting exceptions or overrides.
- Use a Centralized Platform: While you can use native cloud provider tools, a dedicated scheduling platform like Cloud Toggle simplifies management. It offers a user-friendly interface, allows for granular control, and can provide non-engineers with self-service override capabilities without granting them full cloud account access.
For example, a quality assurance team can schedule their Azure VMs to run only from 9 AM to 6 PM on weekdays. If a tester needs to run a late-night test, a platform like Cloud Toggle allows them to temporarily power on a specific VM for a few hours without needing to file a ticket with the DevOps team. This blend of automation and flexibility makes it one of the most powerful strategies to reduce costs.
2. Outsourcing and Offshore Operations
A powerful strategy to reduce costs involves transferring specific business functions or services to external vendors, often in different geographic locations. By leveraging global talent pools and regional cost differences, companies can significantly lower expenses related to labor, infrastructure, and operations. This approach allows organizations to focus on their core competencies while relying on specialized partners for non-critical or resource-intensive tasks.
Outsourcing and offshoring are proven methods for achieving operational efficiency and predictable spending. Handing over functions like IT support, software development, or customer service to a third party can unlock substantial savings and provide access to specialized skills without the overhead of direct hiring.
Key Insight: Depending on the function and location, outsourcing or offshoring can reduce associated labor and operational costs by 20% to 40%. The key is to select the right partner and transfer functions that are well-defined and not central to your company’s unique value proposition.
How to Implement Outsourcing and Offshoring
Successfully transitioning functions to an external partner requires careful planning and a structured approach to mitigate risks and ensure a high return on investment.
- Identify and Vet Potential Functions: Start by identifying non-core business processes that are standardized and can be easily managed remotely. Good candidates include routine IT maintenance, Tier 1 customer support, or quality assurance testing.
- Establish Clear SLAs and KPIs: Define your expectations in a detailed Service Level Agreement (SLA). Specify key performance indicators (KPIs) for quality, response time, and output to ensure the vendor’s performance aligns with your business goals.
- Plan a Phased Transition: Avoid a disruptive "big bang" approach. Instead, plan a careful, phased transition with a clear change management strategy. This allows your internal teams to adapt and provides an opportunity to refine processes with the vendor.
- Maintain Oversight: While you delegate tasks, you should not delegate responsibility. Maintain a core team of in-house experts to manage the vendor relationship, monitor performance, and ensure quality control remains high. This oversight is crucial for making outsourcing one of the most effective strategies to reduce costs.
3. Energy Efficiency and Utility Management
One of the most foundational strategies to reduce costs involves a critical look at physical infrastructure and its energy consumption. From data centers to office buildings, utility bills represent a substantial and often unmanaged operational expense. Implementing technologies and practices to reduce energy consumption in facilities and operations is a powerful lever for immediate and long term savings.

This approach involves a systematic review of how your organization uses power, water, and other utilities, followed by targeted improvements. These can range from low cost changes like retrofitting lighting to significant investments in smart building systems or renewable energy, all contributing to a more resilient and cost efficient operation.
Key Insight: A comprehensive energy efficiency program can be a major competitive advantage. Most organizations discover they can reduce their total energy costs by 10% to 30% through a combination of no cost behavioral changes, low cost upgrades, and strategic investments in new technology.
How to Implement Energy and Utility Management
Launching an energy management initiative is a practical process that generates tangible financial returns while improving your company's environmental footprint.
- Conduct an Energy Audit: The first step is to understand your current consumption patterns. A professional energy audit will identify key areas of waste and provide a prioritized list of potential improvements, from HVAC optimization to equipment upgrades.
- Implement Low-Cost Changes First: Focus on high impact, low cost fixes to build momentum. This could include installing LED lighting, adding programmable thermostats, or sealing air leaks in buildings. These quick wins demonstrate immediate value.
- Leverage Smart Technology: Use smart metering and building management systems to gain real time visibility into energy usage. A centralized platform can automate HVAC and lighting schedules, track consumption against benchmarks, and alert you to anomalies, ensuring continuous optimization.
For instance, after an audit, a manufacturing facility might replace its outdated lighting with energy efficient LEDs, saving thousands annually. It could then implement a policy for powering down non essential machinery after hours, tracked via smart meters. These systematic strategies to reduce costs not only lower utility bills but also extend the lifespan of critical equipment.
4. Supply Chain Optimization
Beyond direct operational and IT spending, optimizing your supply chain offers a profound opportunity to reduce foundational business costs. This involves a strategic overhaul of procurement, inventory management, and logistics to minimize waste, lower material expenses, and enhance delivery efficiency. By streamlining how you source, store, and move goods, you can unlock significant savings and build a more resilient operation.
This holistic approach moves beyond simply finding the cheapest supplier. It focuses on creating an efficient, responsive, and cost-effective network through analytics, vendor consolidation, and strategic sourcing. For many businesses, particularly those in manufacturing, retail, or e-commerce, this is one of the most impactful strategies to reduce costs.
Key Insight: A well-executed supply chain optimization initiative can drive cost reductions of 5-25%. This is achieved by negotiating better terms, reducing excess inventory holding costs, and minimizing transportation and logistics expenses.
How to Implement Supply Chain Optimization
Getting started with supply chain optimization requires a data-driven approach and strong supplier relationships.
- Consolidate Your Supplier Base: Analyze your procurement data to identify opportunities for vendor consolidation. Reducing the number of suppliers you work with can increase your purchasing power, leading to better volume discounts and more favorable contract terms.
- Implement Demand Forecasting: Use historical sales data and market trends to predict future demand more accurately. This allows you to optimize inventory levels, preventing costly overstocking or stockouts that lead to lost sales.
- Establish Supplier Performance Metrics: Develop supplier scorecards to track key metrics like on-time delivery, quality, and cost-effectiveness. This data enables you to have more productive negotiations and make informed decisions about which partnerships to prioritize.
For instance, a retail company can use an e-procurement system to automate purchasing and consolidate orders with its top-performing suppliers, like Procter & Gamble did to streamline its global procurement. This centralizes spending control and leverages analytics to secure better pricing, directly improving the bottom line and demonstrating a powerful strategy to reduce costs.
5. Automation and Robotics Implementation
One of the most transformative strategies to reduce costs involves replacing repetitive, manual tasks with automated systems and robotics. From manufacturing assembly lines to back-office data entry, automation drives down operational expenses by minimizing labor requirements, reducing human error, and increasing overall productivity. This approach allows businesses to operate 24/7 with consistent quality and speed, fundamentally changing their cost structure.

This implementation spans various functions. For example, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solutions from vendors like UiPath and Blue Prism can automate tasks like invoice processing and data migration, while physical robots, like those used in Amazon's fulfillment centers, optimize logistics and material handling. By deploying these technologies, companies can achieve significant, long-term savings.
Key Insight: Implementing automation can reduce operational costs for targeted processes by 20% to 50%. The initial investment is often recouped through increased throughput, improved accuracy, and a dramatic reduction in recurring labor expenses, making it a powerful long-term strategy.
How to Implement Automation and Robotics
Successfully integrating automation requires a strategic, phased approach to maximize return on investment and ensure smooth adoption.
- Identify High-Impact Areas: Start by analyzing business processes to find repetitive, high-volume, and rule-based tasks. These are prime candidates for automation as they offer the quickest and most significant returns.
- Conduct a Thorough ROI Analysis: Before committing, perform a detailed cost-benefit analysis. Factor in software licensing, hardware costs, implementation services, and employee training against projected savings from reduced labor, increased speed, and fewer errors.
- Plan for Change Management: Communicate the benefits of automation to your team early and often. Invest in retraining and upskilling programs to transition employees from manual tasks to higher-value roles, such as overseeing and optimizing the new automated systems.
For instance, a company could start by deploying RPA bots to handle its accounts payable process, automating data extraction from invoices and entry into an accounting system. Once successful, it could expand automation to other administrative functions. This phased rollout minimizes risk and builds momentum, making it one of the most effective strategies to reduce costs while scaling operations.
6. Renegotiating Contracts and Vendor Agreements
While optimizing internal resources is critical, one of the most impactful strategies to reduce costs involves looking outward at your existing vendor agreements. Many organizations set up contracts for software, services, and infrastructure and let them auto-renew without re-evaluation. Systematically reviewing and renegotiating these agreements with vendors and service providers can unlock substantial savings without compromising service quality.
This strategic approach involves more than just asking for a lower price; it's about re-aligning the contract's terms, service levels, and duration with your current business needs. By leveraging market data and performance metrics, you can often secure better pricing, more favorable payment terms, or improved service level agreements (SLAs).
Key Insight: A disciplined approach to contract review can yield significant returns. Businesses that proactively renegotiate can often achieve savings of 5-20% on existing contracts, directly boosting their bottom line without any changes to the services they receive.
How to Implement Contract Renegotiation
Successfully renegotiating vendor agreements requires preparation, data, and a clear strategy.
- Benchmark Your Contracts: The first step is to gather market data. Use industry benchmarks to understand what other companies are paying for similar services. This data provides objective leverage and shifts the conversation from a simple request to a data-driven discussion.
- Consolidate and Leverage Volume: If you have multiple contracts with a single vendor or for similar services across different departments, bundle them together. Presenting a larger, consolidated contract gives you more negotiation power and often qualifies you for volume discounts.
- Document Everything: Track all service performance metrics against the agreed-upon SLAs. If a vendor is underperforming, this documentation is a powerful tool for negotiating a price reduction or securing service credits. It also helps in discussions with partners like managed service providers. For more details, you can learn more about how a managed service provider for AWS can help navigate these complexities.
For example, a tech company can analyze its software-as-a-service (SaaS) usage and find that only 60% of its licensed seats are actively used. Armed with this data, the procurement team can renegotiate its enterprise license agreement to better reflect actual usage, leading to immediate cost reductions. This proactive management is one of the most effective strategies to reduce costs across the entire organization.
7. Digital Transformation and Cloud Migration
One of the most foundational strategies to reduce costs is to shift away from traditional on-premise infrastructure toward modern, cloud-based solutions. This process, often called digital transformation, involves migrating applications, data, and workflows to the cloud and adopting Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) tools. This move fundamentally changes an organization's cost structure from high capital expenditures (CapEx) to more flexible operational expenditures (OpEx).
By moving to the cloud, companies eliminate the substantial costs associated with purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading physical hardware. It also reduces expenses related to real estate for data centers, power, cooling, and the specialized IT staff required to manage them. As demonstrated by companies like Netflix and Airbnb, leveraging cloud infrastructure provides scalability and resilience that is nearly impossible to achieve with on-premise setups, all while optimizing operational spending.
Key Insight: Migrating from on-premise data centers to the cloud can reduce total IT infrastructure and staffing overhead by 20-40%. This is achieved by converting large, fixed capital costs into variable operating costs that scale directly with business needs, preventing over-provisioning and waste.
How to Implement Cloud Migration
A successful cloud migration is a strategic initiative that requires careful planning and execution to maximize its cost-saving potential.
- Plan a Phased Approach: Begin by migrating low-risk, non-critical applications to the cloud. This allows your team to gain experience and build confidence before tackling more complex, mission-critical systems. This gradual approach minimizes disruption and validates your strategy.
- Invest in Training and Governance: Equip your employees with the necessary cloud skills through training and certification programs. Simultaneously, establish clear governance policies for resource creation, tagging, and security to prevent cost overruns and security vulnerabilities from the start.
- Monitor and Optimize Relentlessly: Once in the cloud, cost management is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Use cost management tools to continuously monitor spending, identify inefficiencies, and apply optimization techniques. This proactive stance is a key part of any effective cloud cost optimisation strategy. Learn more about how to maintain cost efficiency post-migration.
For instance, a mid-sized manufacturing company can start its digital transformation by migrating its email and collaboration tools to a SaaS provider like Microsoft 365. The success and cost savings from this initial step can then fund the more complex migration of its inventory management system to a platform like AWS or Azure, turning a major capital expense into a predictable operational cost.
8. Headcount Reduction and Workforce Optimization
While often a last resort, strategically managing workforce size is one of the most direct strategies to reduce costs. This approach involves more than just layoffs; it encompasses a thorough review of organizational structure, roles, and productivity to ensure labor is allocated effectively and efficiently. When executed with care and clear strategy, it can yield significant, immediate savings in payroll and associated benefits.
Workforce optimization focuses on aligning employee roles with core business objectives, eliminating redundancies, and improving overall productivity per employee. Companies like General Motors and Intel have used these initiatives during restructuring to streamline operations, reduce overhead, and refocus on high-growth areas, demonstrating its potential for profound financial impact.
Key Insight: Labor is frequently the largest operational expense for a business. A targeted 10-15% reduction in headcount or workforce-related costs can have a more substantial and immediate impact on the bottom line than many other operational tweaks combined.
How to Implement Workforce Optimization
Approaching headcount reduction requires careful planning, empathy, and strategic communication to minimize disruption and maintain morale among remaining staff.
- Analyze Roles and Redundancies: Before making any decisions, conduct a detailed analysis of all roles and responsibilities. Identify areas of overlap, non-essential functions, and opportunities for consolidation. The goal is to optimize the structure, not just cut numbers.
- Communicate with Transparency: Clearly articulate the business rationale behind the decisions to all employees. Transparency can help mitigate uncertainty and maintain trust, even during a difficult transition.
- Provide Strong Support: Offer generous severance packages, outplacement services, and health benefits to departing employees. For remaining staff, invest in engagement, provide clear paths for growth, and ensure knowledge transfer processes are in place to prevent operational gaps.
- Focus on the Future: Use the restructuring as an opportunity to retrain and upskill remaining employees, aligning their capabilities with the company's future direction. This shifts the focus from simple cost-cutting to strategic realignment.
9. Waste Reduction and Sustainability Initiatives
While often viewed through an environmental lens, waste reduction is a powerful financial lever and one of the most practical strategies to reduce costs. By systematically eliminating waste in materials, resources, and operational processes, organizations can unlock significant savings. This approach extends beyond simple recycling to include optimizing packaging, improving resource efficiency, and rethinking the entire product lifecycle.
Adopting sustainability initiatives creates a culture of efficiency that permeates the entire business. It encourages teams to find innovative ways to use fewer resources, which directly translates to lower material and operational expenditures. Organizations like Unilever and Patagonia have demonstrated that a commitment to sustainability can drive both environmental and economic benefits.
Key Insight: A focused waste reduction program can lead to direct savings of 5-15% in material and operational costs. These initiatives also enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, creating a dual benefit of cost savings and market advantage.
How to Implement Waste Reduction Initiatives
Launching a successful sustainability program involves a strategic, data-driven approach rather than isolated efforts.
- Conduct a Waste Audit: The first step is to understand what you are wasting. A comprehensive audit will identify the types and sources of waste across your operations, providing a clear baseline for setting improvement goals.
- Set Measurable Targets: Establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for waste reduction. For example, aim to reduce packaging material by 10% within one year or achieve a 50% recycling rate for office waste.
- Engage and Empower Employees: Foster a culture of sustainability by involving employees at all levels. Create green teams, offer incentives for innovative waste-saving ideas, and provide training on new processes and policies.
- Optimize and Innovate: Re-evaluate packaging designs to use less material or switch to sustainable alternatives. In the digital realm, this same mindset applies to eliminating "digital waste" like underutilized cloud resources. For instance, addressing the hidden cost of idle VMs is a key part of a digital sustainability strategy.
By treating waste not as a byproduct but as a sign of inefficiency, companies can implement highly effective strategies to reduce costs. A retailer, for example, might optimize its supply chain to reduce product spoilage, directly cutting losses and improving its bottom line. This holistic view turns sustainability from a cost center into a core component of financial health.
10. Embrace Shared Services and Centralization
Organizational redundancy is a major, often hidden, driver of high administrative costs. When each business unit or department manages its own HR, IT, Finance, and Procurement, it creates duplicated effort, inconsistent processes, and siloed expertise. Centralizing these back office functions into a shared services model is a powerful strategy to reduce costs by streamlining operations.
This approach involves creating a single, internal entity responsible for delivering specific business-support services across the entire organization. By consolidating these functions, you eliminate redundant roles, standardize procedures, and leverage economies of scale, leading to significant efficiency gains and cost savings.
Key Insight: Companies that successfully implement a shared services model can reduce their general and administrative (G&A) expenses by 15-30%. This is achieved by optimizing processes, improving resource utilization, and leveraging technology more effectively across the organization.
How to Implement a Shared Services Model
Transitioning to a centralized model requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth and successful rollout.
- Map Existing Processes: Before centralizing, conduct a thorough analysis of current processes within each function (IT, HR, Finance). Identify inefficiencies, variations, and opportunities for standardization. This mapping forms the blueprint for your new, optimized model.
- Establish Clear SLAs: Define Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with the business units you will be serving. These agreements should clearly outline the scope of services, performance metrics (KPIs), and response times, ensuring accountability and maintaining service quality.
- Invest in Technology and Change Management: A successful shared services center relies on robust technology to automate and manage workflows. Equally important is a comprehensive change management plan to communicate benefits, train staff on new processes, and manage the transition for all stakeholders.
For example, a company might consolidate IT support from three separate departmental teams into one central helpdesk. This single team uses a unified ticketing system, follows standardized procedures for troubleshooting, and manages hardware procurement for the entire organization. This not only cuts down on staff and system redundancies but also provides a consistent and measurable level of IT support for all employees, making it a highly effective strategy to reduce costs.
Comparison of 10 Cost-Reduction Strategies
| Strategy | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lean Manufacturing and Process Optimization | High cultural change, training | Moderate training, mapping tools, time | 15–30% cost reduction; improved quality & cycle time | Manufacturing, production lines, warehouses | Eliminates waste, better inventory control, employee engagement |
| Outsourcing and Offshore Operations | Medium–High vendor selection, governance | Low capital, high vendor management & legal oversight | 20–40% labor/operational cost savings; scalability | Non-core functions: IT, customer support, labor-heavy ops | Labor arbitrage, access to expertise, flexible scaling |
| Energy Efficiency and Utility Management | Medium audits, tech upgrades | High upfront capital for LED/HVAC/automation; ongoing maintenance | 10–30% energy cost reduction; sustainability gains | Facilities, data centers, retail stores, large offices | Sustained energy savings, tax incentives, improved comfort |
| Supply Chain Optimization | High data integration, sourcing changes | Moderate–High analytics tools, process redesign | 5–25% procurement/material cost savings; better cash flow | Retailers, manufacturers, procurement-heavy firms | Lower material costs, improved visibility, supplier relations |
| Automation and Robotics Implementation | High integration, technical complexity | Very high capital & skilled personnel | 20–50% operational cost reduction; higher throughput & accuracy | Repetitive/high-volume manufacturing, back-office automation | 24/7 operation, reduced errors, strong productivity gains |
| Renegotiating Contracts and Vendor Agreements | Low–Medium negotiation effort | Low benchmarking, legal support | 5–20% savings on existing contracts; minimal disruption | Near-term renewals, supplier-heavy spend categories | Quick wins, low implementation cost, improved contract terms |
| Digital Transformation and Cloud Migration | High migration complexity & integration | High IT skills, migration tools, ongoing subscriptions | 20–40% IT cost reduction; improved scalability & insights | Legacy IT modernization, SaaS adoption, scalable services | Reduced CapEx, flexibility, better disaster recovery |
| Headcount Reduction and Workforce Optimization | Medium legal/HR complexity | Moderate severance, analytics, change programs | 10–30% immediate payroll savings; potential long-term risks | Financial pressure, role redundancy, efficiency drives | Rapid cost reduction, leaner structure, faster implementation |
| Waste Reduction and Sustainability Initiatives | Medium program setup, behavior change | Low–Moderate audits, recycling systems, process tweaks | 5–15% material cost savings; lower disposal costs | Product manufacturers, retailers, companies with packaging waste | Cost savings plus improved brand, regulatory compliance |
| Shared Services and Centralization of Functions | High restructuring & change management | Moderate–High systems, transition costs, training | 15–30% administrative cost savings; standardization | Large orgs with duplicated back-office functions | Economies of scale, standardized processes, improved compliance |
Turning Strategy into Sustainable Savings
Navigating the landscape of operational expenses can feel like a complex, unending battle against a rising tide. Yet, as we have explored through these ten distinct strategies, the power to reclaim control over your budget is firmly within your grasp. The journey from identifying potential savings to realizing them in your bottom line is not about a single, revolutionary change. Instead, it is about the methodical and consistent application of diverse, targeted tactics. From the foundational principles of Lean Manufacturing to the forward-thinking implementation of Digital Transformation, each approach offers a unique lever to pull in your quest for financial efficiency.
The core lesson is that meaningful cost reduction is a multifaceted discipline. It requires a holistic view that connects process optimization in one department with supply chain logistics in another. It demands a cultural shift where every team member, from the plant floor to the executive suite, is empowered to identify and eliminate waste. These are not just isolated projects; they are interconnected components of a larger, more resilient operational framework. Implementing strategies to reduce costs effectively means building a system where efficiency is not an afterthought but the default state of being.
From Insights to Actionable Impact
The true value of this exploration lies in its practical application. It is easy to acknowledge the potential of Automation, Shared Services, or Energy Management in theory. The challenge, and the opportunity, is to translate these concepts into concrete actions that yield measurable results. A successful cost-reduction initiative is built on momentum. Start with the "quick wins" that generate immediate value and build confidence across the organization.
For instance, renegotiating a single vendor contract or optimizing one high-energy process can free up capital and demonstrate the power of proactive management. These early victories create the buy-in needed to tackle more complex, long-term initiatives like a full-scale cloud migration or the centralization of key business functions. Remember, the goal is not just to cut costs for a single quarter but to embed a culture of continuous improvement that delivers sustainable savings year after year.
Key Takeaways for Building a Cost-Conscious Culture
To synthesize the crucial lessons from our discussion, focus on these foundational pillars as you move forward:
- Visibility is the First Step: You cannot optimize what you cannot see. Whether it is a detailed energy audit, a supply chain analysis, or a comprehensive cloud asset inventory, granular visibility is the non-negotiable prerequisite for effective cost management.
- Empowerment Drives Innovation: The best ideas for reducing waste and inefficiency often come from the teams closest to the work. Foster an environment where employees are encouraged and rewarded for bringing forward cost-saving suggestions.
- Technology is a Catalyst, Not a Cure-All: Automation, cloud services, and advanced analytics are powerful tools. However, they are most effective when applied to well-defined processes. Technology should enhance a sound strategy, not compensate for a flawed one.
- Sustainability and Savings are Aligned: As demonstrated by strategies like waste reduction and energy efficiency, initiatives that are good for the planet are often excellent for your budget. This alignment provides a powerful narrative for engaging both employees and customers.
Ultimately, mastering these strategies to reduce costs transforms your approach to financial management from a reactive, defensive posture into a proactive, strategic advantage. By weaving these principles into the fabric of your organization, you are not merely trimming expenses. You are building a more agile, resilient, and competitive enterprise prepared to thrive in any economic climate. The path to sustainable savings is an ongoing journey, and with these strategies as your guide, you are well-equipped to begin.
Ready to capture one of the most significant and often overlooked sources of savings in your cloud budget? CLOUD TOGGLE provides the simplest way to eliminate wasted spend on idle development, staging, and QA resources. Get started in minutes and see how automated scheduling can transform your cloud bill at CLOUD TOGGLE.