Figuring out Amazon S3 costs can feel like you're trying to solve a puzzle. The final price tag isn't just about how much data you're storing. It's a mix of storage, how often you access that data, and where you move it, which makes a simple per-gigabyte price pretty misleading.
Understanding Your Amazon S3 Bill
Think of your S3 bill like your home electricity bill. You don't just pay a flat fee for being on the grid. You pay for how much power you use, when you use it, and maybe even how fast you need it during peak times. In the same way, S3 charges for a lot more than just the digital "space" your files take up.
If you want to get a real handle on your spending, you have to look at the whole picture. Your total bill is the sum of a few different parts, and each has its own pricing rules. If you ignore any one of these, you're setting yourself up for a nasty surprise at the end of the month.
The Core Components of S3 Pricing
At a high level, a few key things drive most of your S3 bill. Getting these down is the first big step toward trimming your costs.
- Storage Volume: This is the easy one. You pay for the amount of data you store in your S3 buckets, measured in gigabytes (GB), over the course of a month.
- Data Requests: Every time you or your application does something with your data, like uploading (PUT), downloading (GET), or listing files (LIST), it’s a request. AWS charges a tiny fee for each of these actions.
- Data Transfer: This one can be a silent killer. Moving data out of S3 to the internet or even to a different AWS region costs money. If you're serving content to a global audience, this can add up fast.
A simple way to think about it: Storage is the rent for your warehouse space. Requests are the fees you pay staff to go get items off the shelves. Data transfer is the shipping cost to send those items out to your customers.
Here's a quick breakdown of those main cost drivers.
Primary Amazon S3 Cost Drivers at a Glance
This table gives you a snapshot of the key pieces that make up your total S3 bill.
| Cost Component | What You Pay For | Example Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | The amount of data stored in your S3 buckets. | Price per GB per month |
| Requests & Data Retrievals | Operations performed on your data, like uploads or downloads. | Price per 1,000 requests |
| Data Transfer Out | Moving data from S3 to the internet or another AWS Region. | Price per GB transferred |
| Management & Replication | Features like S3 Inventory, Analytics, and Replication. | Price per object or per GB |
| Data Processing | Services that process data directly, like S3 Object Lambda. | Price per GB processed |
Each of these components plays a role, so keeping an eye on all of them is crucial for effective cost management.
Beyond the Basics of Storage Fees
The real complexity with amazon s3 costs comes from how these pieces interact with your specific usage patterns. For example, storing 1 TB of data might look cheap on paper. But if thousands of users are constantly accessing and downloading that data all over the world, your costs can explode. You can find a more detailed breakdown of the cost of Amazon S3 that dives into these specifics.
This is exactly why just picking the cheapest storage tier isn't always the smartest move. If you dig a little deeper, you'll find huge savings by matching your data's access patterns to the right pricing model.
For instance, companies that get strategic with storage tiers and lifecycle policies can save a fortune. A great real-world example is Canva. They reported saving over $3 million a year by shifting massive amounts of data to S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval, a storage class built for data that isn't accessed often but still needs to be available instantly. You can read the full story about Canva's S3 cost savings on the official AWS blog to see how they did it.
Getting this foundational model right is everything. It shifts you from just passively paying your AWS bill to actively managing it, making sure you're only paying for what you actually need.
Choosing the Right S3 Storage Class
Not all data is created equal, and AWS prices its storage accordingly. The best way to think about this is like a self-storage facility. You keep things you need daily in a locker right by the front door for easy access. Long-term keepsakes you only check on once a year? Those can go on a cheaper pallet deep in the back of the warehouse.
Amazon S3 offers a similar range of choices, called Storage Classes, designed to match how you use your data with the right price point. Picking the right one is probably the single biggest move you can make to get your amazon s3 costs under control.
Putting rarely used backup files in a high-performance tier is like paying premium rent on a storefront just to store old furniture, a total waste of money. On the flip side, if you stick your website's active images in a slow, cheap archive tier, you'll frustrate users and hurt your business.
The whole game is a trade-off. Generally, as the price per gigabyte of storage drops, the cost and the time it takes to get that data back go up. Let's break down the main options to figure out which "storage unit" fits your needs.
This diagram helps visualize how your total S3 bill is a mix of storage, requests, and data transfer fees, all of which are directly affected by the storage class you choose.
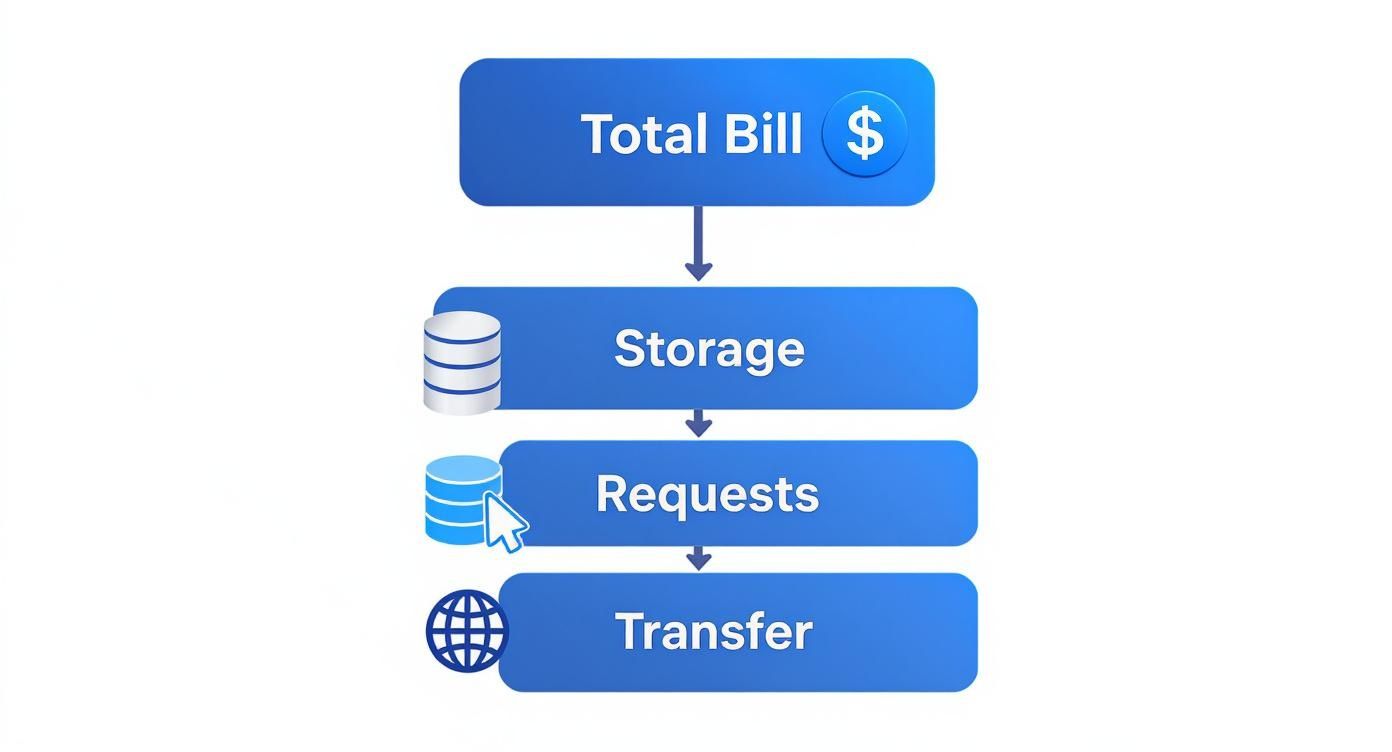
As you can see, your choice has ripple effects beyond just the monthly storage fee; it impacts what you pay every time you touch or move your data.
S3 Standard for Frequently Accessed Data
S3 Standard is the default for a reason. It’s that front-access locker we talked about, built for "hot" data that gets hit all the time and needs to be retrieved in milliseconds.
- Best For: Dynamic websites, content delivery networks (CDNs), mobile apps, and big data analytics workloads.
- Performance: It's designed for high durability, high availability, and the lowest possible latency.
- Cost Structure: This class has the highest storage cost per gigabyte but charges the least for access. That makes it perfect for data with heavy, consistent traffic.
When in doubt, S3 Standard is always a safe bet for any application where performance is key.
S3 Intelligent-Tiering for Unpredictable Access
But what if you have data with access patterns that are all over the place? That’s where S3 Intelligent-Tiering shines. It acts like a smart warehouse manager, automatically moving your data between frequent and infrequent access tiers behind the scenes. You get the cost savings without any performance hit or manual work.
Think of S3 Intelligent-Tiering as a helpful robot that moves your boxes from expensive, easy-to-reach shelves to cheaper backroom shelves based purely on how often you ask for them.
This is the ideal solution for data where usage can swing from daily to monthly without any warning. You pay a small monthly fee for the monitoring and automation, but it almost always pays for itself by making sure you're never overpaying for storage.
Infrequent Access Classes S3 Standard-IA and One Zone-IA
For data you don't touch often but need back quickly when you do, AWS provides two "Infrequent Access" (IA) tiers. These are fantastic for things like long-term backups, older user-generated content, and disaster recovery files.
- S3 Standard-IA (Infrequent Access): This gives you the same durability and low latency as S3 Standard, but with a lower per-GB storage price. The catch? You'll pay a higher fee to retrieve the data. It’s built for data you might access once a month.
- S3 One Zone-IA: This is an even cheaper option because it stores your data in a single AWS Availability Zone instead of replicating it across multiple zones. This makes it less resilient, so it’s best for non-critical data you can easily reproduce, like secondary backup copies or thumbnail images.
Choosing an IA class is a smart, deliberate move to save money on data you know will sit untouched most of the time.
The Glacier Family for Archiving
When it comes to long-term data archiving at the absolute lowest cost, the S3 Glacier family is your answer. These are the deep warehouse pallets, built for data you might need to pull out once or twice a year, if ever.
- S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval: Offers the lowest storage cost for archived data that you still need back in milliseconds.
- S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval: An even cheaper choice, but retrieval can take anywhere from a few minutes to several hours.
- S3 Glacier Deep Archive: This is the cheapest storage in all of AWS, period. Retrievals can take up to 12 hours. It's designed for data you have to keep for legal or compliance reasons but will almost certainly never access again.
These archive tiers deliver huge savings on storage, but the retrieval fees and delays are significant. They're only suitable for true archival workloads.
To help you visualize the differences, here’s a quick comparison of the main storage classes.
Comparing Amazon S3 Storage Classes
The table below breaks down the primary S3 storage classes, showing their best-fit use cases, typical retrieval times, and how their costs compare for storage versus retrieval.
| Storage Class | Ideal Use Case | Retrieval Time | Relative Storage Cost | Relative Retrieval Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S3 Standard | Active websites, analytics, mobile apps | Milliseconds | Highest | Lowest |
| S3 Intelligent-Tiering | Data with unknown or changing access | Milliseconds | Varies | Varies |
| S3 Standard-IA | Long-term backups, disaster recovery | Milliseconds | Lower | Higher |
| S3 One Zone-IA | Replicable data, secondary backups | Milliseconds | Lower | Higher |
| S3 Glacier Instant | Archiving with fast access needs | Milliseconds | Very Low | High |
| S3 Glacier Flexible | Archiving with flexible retrieval | Minutes to Hours | Very Low | High |
| S3 Glacier Deep Archive | Compliance, long-term preservation | Hours | Lowest | Highest |
Choosing the right class is all about balancing how much you want to save on storage against how much you're willing to pay, in both money and time, when you need that data back.
It's also worth noting how S3 pricing tiers on the AWS website have simplified over time. In the old days, S3 had complex pricing tiers that gave steep discounts to massive users. Since December 1, 2016, however, the structure has become much flatter, making cost estimates far more predictable. For example, you might pay $0.023/GB for your first 50 TB, $0.022/GB for the next 450 TB, and $0.021/GB for anything over 500 TB per month. This change has made managing cloud storage expenses much more straightforward for everyone.
Uncovering Hidden S3 Cost Drivers
When your Amazon S3 costs start creeping up, it's natural to blame storage and data transfer fees. They're the usual suspects, after all. But often, the real culprits are the less obvious charges that quietly inflate your monthly bill.
These "hidden" costs usually come from powerful S3 features that, while incredibly useful, have their own pricing models. Getting a handle on them is the key to avoiding bill shock and making sure you only pay for what you actually need.

It’s a bit like buying a car. You see the sticker price, but that’s just the start. You also have to factor in insurance, gas, and regular maintenance. With S3, features for management and analytics are those ongoing operational costs that can easily catch you by surprise if you're not paying attention.
The Price of Data Management and Analytics
AWS provides a whole suite of tools to help you understand what's going on with your storage, but these insights aren't always free. They offer tremendous value by flagging optimization opportunities, but it's critical to understand how they add to your bill.
- S3 Storage Lens: This is a fantastic analytics tool for organization-wide visibility into storage usage. While there’s a free tier, the really useful advanced metrics and recommendations come at a price, typically billed per million objects monitored each month.
- S3 Inventory Reports: Need a detailed CSV list of all your objects and their metadata? S3 Inventory is your go-to. Just remember that generating these reports is a billable action, charged per million objects listed.
- S3 Analytics Storage Class Analysis: This feature is great for figuring out when to move data to a cheaper storage class by watching access patterns. Like the other tools, it charges a small fee for every million objects it monitors.
Individually, these charges might look like pocket change. But if you have buckets with billions of objects, they can quickly add up to a significant expense. For a deeper dive into how these and other services can create surprise bills, check out our guide on unexpected AWS charges.
The Compounding Cost of S3 Versioning
S3 Versioning is an amazing safety net. It protects you from accidentally deleting or overwriting important files by keeping multiple copies of an object every time it changes. When you enable it, overwriting a file doesn't actually replace it; S3 just creates a new version and tucks the old one away.
This is a lifesaver for data protection, but it has a direct, and often overlooked, impact on your storage bill.
If you enable versioning on a 100 GB bucket and then overwrite every single file, you are now paying for 200 GB of storage. Do it again, and you're at 300 GB. The cost can multiply fast without good housekeeping.
The tricky part is that these old versions are invisible unless you go looking for them. They just sit there, racking up storage charges forever until you either delete them manually or, better yet, set up a lifecycle policy to automatically clean them out after a set time.
The Double Expense of Replication
For disaster recovery or compliance, S3 Replication is a must-have. It automatically copies objects from a source bucket to a destination bucket, which can be in the same AWS Region or a different one entirely. This keeps your data safe even if a whole region has a bad day.
But this resilience comes at a very clear price. When you turn on replication, you're essentially paying for your storage twice over.
- Duplicate Storage Costs: You pay to store the data in the source bucket and you pay to store the identical copy in the destination bucket.
- Data Transfer Fees: If you're using Cross-Region Replication (CRR), you'll also get hit with inter-region data transfer fees for every gigabyte copied across.
- Request Charges: The replication process itself generates a high volume of PUT requests, which also add small charges to your bill.
While replication is non-negotiable for critical workloads, it's a major cost multiplier. Understanding these layered charges helps you make smart decisions about which data truly needs this level of redundancy, so you can balance resilience with your budget.
Actionable Strategies for S3 Cost Optimization
Knowing what’s on your bill is one thing, but actually taking control of your Amazon S3 costs requires a hands-on approach. Thankfully, AWS gives you some powerful, and often automated, tools to help you cut down expenses without hurting performance. By putting a few key strategies into play, you can make sure you’re only paying for what you truly need.
These tactics range from setting up automatic data tiering to just doing some good old-fashioned digital housekeeping. The main idea is to build cost efficiency right into your storage setup, rather than treating it like an afterthought.

Let's break down the most effective ways to shrink that monthly S3 bill.
Automate Savings with S3 Lifecycle Policies
One of the best tools in your cost-saving kit is S3 Lifecycle policies. These are basically simple rules you set on a bucket to automatically shift objects to cheaper storage classes or just delete them as they get older.
Think of it like setting up a recurring order for your data. You can tell S3, "After 30 days, move all these log files from S3 Standard to S3 Standard-IA. Then, after 180 days, archive them in S3 Glacier Deep Archive. And finally, get rid of them completely after seven years."
This "set it and forget it" method is perfect for data with predictable lifecycles, like backups, logs, or old project files. By setting up these policies, you avoid the nightmare of manually managing millions of objects and guarantee you're always on the most cost-effective storage tier.
Embrace S3 Intelligent-Tiering for Unpredictable Data
But what about data where you have no idea when it'll be accessed? That's where S3 Intelligent-Tiering becomes your new best friend. Instead of you making the rules, this storage class keeps an eye on how each object is used and automatically moves it between frequent and infrequent access tiers for you.
S3 Intelligent-Tiering is like having an automated financial advisor for your data. It constantly rebalances your storage portfolio to get you the best savings without you lifting a finger, taking all the guesswork out of the equation.
You do pay a small monthly fee for this monitoring, but for workloads with changing access patterns, the savings almost always make it worthwhile. It's the perfect fit for user-generated content, analytics datasets, or any collection of files where usage is all over the place.
Conduct Regular Storage Housekeeping
Sometimes the biggest savings come from the simplest actions. Over time, your S3 buckets can fill up with junk that quietly drives up your bill. Auditing your storage on a regular basis is a must for keeping Amazon S3 costs down.
Here are a few key things to look for during your cleanup:
- Delete Incomplete Multipart Uploads: When a large file upload fails, S3 can leave behind orphaned parts. You can't see these in the normal bucket view, but you're still paying for them. A simple lifecycle rule can automatically delete these after a day or two.
- Remove Old Object Versions: If you have versioning turned on, old file versions will hang around forever unless you tell S3 to clean them up. A lifecycle policy can automatically expire noncurrent versions after a set time, like 90 days.
- Identify and Delete Unused Buckets: It's shockingly easy for old test buckets or forgotten project buckets to sit there for years, costing you money. Use tools to find buckets with no recent activity and just delete them.
These simple housekeeping tasks can lead to some quick and noticeable savings. For a deeper dive into managing your cloud budget, you might find our guide to cloud cost optimisation helpful.
Use Analytics to Pinpoint Savings Opportunities
You can't fix what you can't see. AWS offers tools designed to give you a clear view of your storage usage, helping you find exactly where your money is going and where you can make cuts.
The main tool for this job is S3 Storage Lens. It gives you a dashboard view of your storage usage and activity across your entire organization. You can use it to spot your biggest and fastest-growing buckets, find buckets that are missing lifecycle policies, and track down those incomplete multipart uploads.
For a more granular look, S3 Storage Class Analysis watches access patterns within a single bucket. It collects the data you need to build smarter lifecycle policies, making sure you move data to cheaper tiers at just the right moment.
Mini Case Study: An E-commerce Company
Let's put this into practice. Imagine an e-commerce company that stores millions of product images and daily transaction logs in S3. Their first bill is a shocker because everything is sitting in the pricey S3 Standard class.
Here’s how they could tackle their Amazon S3 costs:
- Product Images: The company notices new product images are accessed a lot for the first 60 days, then barely touched. They set up a lifecycle policy to move images from S3 Standard to S3 Standard-IA after 60 days, immediately cutting storage costs for older images by over 40%.
- Transaction Logs: Access to these logs is totally random. Some are needed right away for fraud checks, while others aren't looked at for months. They switch the whole log bucket to S3 Intelligent-Tiering, letting AWS handle moving data to the cheapest tier based on real-time usage.
- Cleanup: Using S3 Storage Lens, they find a 500 GB staging bucket left over from a website redesign two years ago. They also discover 80 GB of incomplete parts from failed image uploads. By deleting the old bucket and setting a rule to clean up failed uploads, they get an instant cost reduction.
By applying these simple strategies, the company could easily slash its monthly S3 bill by 30-50% without affecting a single customer. It just goes to show how a proactive approach to cost management can deliver real results.
How to Accurately Forecast Your S3 Bill
Trying to budget for Amazon S3 costs without a solid forecast is like flying blind. It's a recipe for some serious bill shock. The good news is that AWS gives you the tools you need to move from guessing to calculating, turning what feels like a random expense into a predictable line item.
The trick is to break down your expected usage into the core cost drivers we’ve already talked about: storage, requests, and data transfers. Once you think through each of these pieces, you can build a reliable financial model for your cloud setup.
Using the AWS Pricing Calculator
Your go-to tool for this is the AWS Pricing Calculator. It’s a free, web-based estimator that walks you through configuring your S3 usage, making sure you don't forget any of the little details that add up on your final bill.
To get a realistic number, you need to plug in a few key data points about your workload. A good forecast is more than just a rough guess about how much storage you’ll use.
Here’s a simple process to get you started:
- Estimate Storage: Start with the total gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB) you plan to store. Don't forget to pick the right S3 Storage Class based on how you'll access the data.
- Project Requests: Think about how your application actually uses the data. How many PUT requests (uploads) and GET requests (downloads) do you expect each month?
- Calculate Data Transfer: This one is a big deal. Estimate how much data will be transferred out of S3 to the public internet. Data transfer in is free, but data going out is a major cost driver.
By carefully considering these three pillars, the calculator will spit out a detailed monthly cost breakdown.
Forecasting Example: Static Website Hosting
Let’s walk through a classic use case: hosting a static website on S3.
Imagine your site has 10 GB of assets (images, CSS, and JavaScript files) all sitting in S3 Standard. You’re expecting 50,000 visitors a month, and each visitor downloads about 2 MB of data on average. To load all that content, your site makes 200,000 GET requests.
Here's how that breaks down:
- Storage Cost: 10 GB in S3 Standard.
- Request Cost: 200,000 GET requests per month.
- Data Transfer Out Cost: 50,000 visitors * 2 MB/visitor = 100,000 MB, which is 100 GB per month.
When you plug these numbers into the AWS Pricing Calculator, you get a clear, actionable monthly estimate. No more guesswork, just effective budgeting.
Tracking and Alerting with AWS Tools
Of course, a forecast is only half the battle. You need to track your actual spending against it. For this, AWS gives you two essential services: AWS Cost Explorer and AWS Budgets.
Think of the AWS Pricing Calculator as your financial map and Cost Explorer as your GPS. The map shows you the route, but the GPS tells you where you are right now and if you’ve taken a wrong turn.
AWS Cost Explorer gives you detailed graphs and reports on your spending. You can filter by service (just show me S3) and even use tags to see which specific buckets or projects are driving up your Amazon S3 costs. It’s the perfect way to see if your forecast was on the mark or if something unexpected is happening.
To make sure you never go over budget, you can set up AWS Budgets. This tool lets you create custom cost thresholds and sends you an alert via email or SMS when you’re getting close. For example, you could set a budget for your total monthly S3 bill and get a notification when you hit 80% of your forecast. This gives you plenty of time to investigate and take action before the bill gets out of hand.
Common Questions About Amazon S3 Costs
Digging into an AWS bill can sometimes feel like solving a puzzle, especially when unexpected S3 charges pop up. It's totally normal to have questions. Getting a handle on these common points of confusion is the key to mastering your S3 spending.
Let's walk through some of the questions that come up most often.
Why Are My S3 Data Transfer Costs So High?
This is a classic. You check your bill and see a huge spike in data transfer fees, leaving you scratching your head.
The culprit is almost always "Data Transfer Out to Internet." While AWS doesn't charge you to upload data into S3, they do charge for every gigabyte that gets downloaded from your S3 bucket to the public internet. Think of it like a toll road: free to get on, but you pay to get off.
The best way to tackle this is with Amazon CloudFront, which is Amazon's Content Delivery Network (CDN). CloudFront works by caching copies of your files in locations all over the world, closer to your users. When someone requests a file, it's served from the nearest cache instead of directly from your S3 bucket. This not only speeds things up for your users but also comes with a much lower data transfer rate, often leading to big savings.
Is S3 Intelligent-Tiering Always the Best Choice?
Intelligent-Tiering is a fantastic default choice, especially when you have no idea how often your data will be accessed. It’s like having a smart assistant that automatically shuffles your files between a "frequently used" shelf and a "rarely used" one to save you money.
But it’s not always the perfect fit. Intelligent-Tiering comes with a small monthly fee for monitoring and automating this process for each object. For predictable workloads, like monthly backups you know won't be touched, it's cheaper to set up a simple Lifecycle Policy. That policy can move the data directly to S3 Standard-IA after 30 days, skipping the monitoring fee altogether.
How Can I Find Which S3 Bucket Is Costing Me the Most?
When you have dozens or even hundreds of buckets, finding the expensive one can feel like looking for a needle in a haystack.
Your go-to tool here is AWS Cost Explorer. It's built right into your AWS console. You can easily filter your costs by service (just pick S3) and then group the bill by "Usage Type" or a resource tag you've applied. This will quickly show you which buckets are racking up the charges.
If you need even more detail, you should enable S3 Storage Lens. This tool gives you an organization-wide view with advanced metrics on your storage. It helps you zoom in on the specific buckets or even prefixes that are driving up your amazon s3 costs.
Using these native tools gives you the visibility you need to stop guessing and start making targeted changes to bring your costs down.
Are idle cloud resources inflating your AWS bill? CLOUD TOGGLE helps you automatically shut down non-production servers on a schedule, cutting costs without impacting your team's workflow. Start your free trial and see how much you can save.